Elderly Patients and Management in Intensive Care Units (ICU): Clinical Challenges
- PMID: 36714685
- PMCID: PMC9879046
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S365968
Elderly Patients and Management in Intensive Care Units (ICU): Clinical Challenges
Abstract
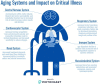
There is a growing population of older adults requiring admission to the intensive care unit (ICU). This population outpaces the ability of clinicians with geriatric training to assist in their management. Specific training and education for intensivists in the care of older patients is valuable to help understand and inform clinical care, as physiologic changes of aging affect each organ system. This review highlights some of these aging processes and discusses clinical implications in the vulnerable older population. Other considerations when caring for these older patients in the ICU include functional outcomes and morbidity, as opposed to merely a focus on mortality. An overall holistic approach incorporating physiology of aging, applying current evidence, and including the patient and their family in care should be used when caring for older adults in the ICU.
Keywords: critical illness; geriatric syndrome; organ dysfunction; respiratory failure; shock.
© 2023 Brunker et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CSB and CGH are consultants for and received fees from Sedana Medical. CGH has received research grant funding from Kohler Chemie. The authors declare no other competing interests for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Mather MJ, Pollard KM. Aging in the United States. Popul Bull. 2015;70(2):1–18.
-
- Halvachizadeh S, Grobli L, Berk T, et al. The effect of geriatric comanagement (GC) in geriatric trauma patients treated in a level 1 trauma setting: a comparison of data before and after the implementation of a certified geriatric trauma Center. PLoS One. 2021;16(1):e0244554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244554 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

