Children with Conductive Hearing Loss Fitted with Hearing Aids: Outcomes and Caregiver Experiences in South Africa
- PMID: 36714894
- PMCID: PMC9879652
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1742769
Children with Conductive Hearing Loss Fitted with Hearing Aids: Outcomes and Caregiver Experiences in South Africa
Abstract
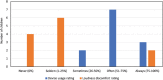
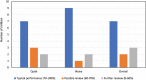
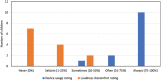
Introduction Hearing aids are a frequent management option for children with conductive hearing loss (CHL) and it is necessary to determine the efficacy of outcomes. Limited information regarding caregivers' perceptions and experiences are available to examine outcomes in this population. Objectives To describe hearing aid outcomes and caregivers' experiences for children with CHL who wear behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids. Methods Retrospective review of clinical data from 19 children between 0 and 13 years of age with CHL, who were fitted with BTE hearing aids between January 2017 and March 2020. Hearing aid outcomes were documented at one month post-hearing aid fitting, via average daily use and caregiver and teacher reports obtained through the Parents' Evaluation of Aural/oral performance of Children (PEACH) and the Teachers' Evaluation of Aural/oral performance of Children (TEACH). Telephonic surveys were conducted with 13 caregivers to explore their experiences. Qualitative data from open-ended questions were analyzed thematically. Results The average hearing aid use was 6.5 hours/day (2.0 standard deviation, SD; range 4.1-10.3) for bilateral hearing aid users. Questionnaire results indicated that most children (PEACH - 83.3% and TEACH - 92.3%) used their hearing aids more than 75% of the time. Participants performed better in quiet environments with limited sensitivity to loud sounds at home and at school. Reported challenges included stigma and device compliance. Conclusions Children with CHL used their hearing aids for comparable hours (5-8 hours/day), as reported for children with sensorineural hearing loss, but less than the recommended 10 hours/day required for adequate language development. Caregivers reported benefits equivalent to expectations, with challenges similar to those reported in high-income countries.
Keywords: caregivers; conductive hearing loss; hearing aids; outcome measures; pediatrics.
Fundação Otorrinolaringologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commecial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes and device use in children with bone-conduction hearing devices in South Africa.S Afr J Commun Disord. 2024 Feb 19;71(1):e1-e8. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v71i1.1005. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 38426736 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of children with sensorineural hearing loss fitted with binaural hearing aids at a pediatric public hospital in South Africa.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Jan;152:110977. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2021.110977. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34802750
-
Pediatric Hearing Aid Management: Parent-Reported Needs for Learning Support.Ear Hear. 2016 Nov/Dec;37(6):703-709. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000338. Ear Hear. 2016. PMID: 27438872
-
Evaluation of Factors Affecting Hearing Aid Use in Children.Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Mar;61(1):25-36. doi: 10.4274/tao.2022.2022-6-9. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37583979 Free PMC article.
-
The University of Western Ontario Pediatric Audiological Monitoring Protocol (UWO PedAMP).Trends Amplif. 2011 Mar-Jun;15(1):57-76. doi: 10.1177/1084713811420304. Trends Amplif. 2011. PMID: 22194316 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Outcomes and device use in children with bone-conduction hearing devices in South Africa.S Afr J Commun Disord. 2024 Feb 19;71(1):e1-e8. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v71i1.1005. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 38426736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization World report on hearing https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/world-report-on-hearing(Accessed June 2021).
-
- Global Research on Developmental Disabilities Collaborators . Olusanya B O, Davis A C, Wertlieb D. Developmental disabilities among children younger than 5 years in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(10):e1100–e1121. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Multi-country assessment of national capacity to provide hearing care http://www.who.int/pbd/publications/WHOReportHearingCare_Englishweb.pdf?...(Accessed July 2021).
-
- World Health Organization Deafness and hearing loss https://www.who.int/pbd/deafness/world-hearing-day/WHD2016_Brochure_EN_2...(Accessed 3 February 2019).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

