Design and In Vitro Evaluation of an Artificial Placenta Made From Hollow Fiber Membranes
- PMID: 36716073
- PMCID: PMC9897463
- DOI: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001862
Design and In Vitro Evaluation of an Artificial Placenta Made From Hollow Fiber Membranes
Abstract
For infants born at the border of viability, care practices and morbimortality rates vary widely between centers. Trends show significant improvement, however, with increasing gestational age and weight. For periviable infants, the goal of critical care is to bridge patients to improved outcomes. Current practice involves ventilator therapy, resulting in chronic lung injuries. Research has turned to artificial uterine environments, where infants are submerged in an artificial amniotic fluid bath and provided respiratory assistance via an artificial placenta. We have developed the Preemie-Ox, a hollow fiber membrane bundle that provides pumpless respiratory support via umbilical cord cannulation. Computational fluid dynamics was used to design an oxygenator that could achieve a carbon dioxide removal rate of 12.2 ml/min, an outlet hemoglobin saturation of 100%, and a resistance of less than 71 mmHg/L/min at a blood flow rate of 165 ml/min. A prototype was utilized to evaluate in-vitro gas exchange, resistance, and plasma-free hemoglobin generation. In-vitro gas exchange was 4% higher than predicted results and no quantifiable plasma-free hemoglobin was produced.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the ASAIO.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: W.J.F. chairs the Scientific Advisory board and is a founder of ALung Technologies, in which he has an equity interest. No other authors have conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
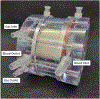

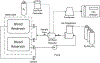
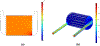


References
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Previable Birth: Obstetric Care Consensus No.6. Obstetric Gynecology 130: e187–99, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Seri I, Evans J: Limits of viability: definition of the gray zone J Perinatol 28: S4–S8, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith J, Karotkin E, Kesler M, Suresh G (eds): Assisted Ventilation of the Neonate: An Evidence-Based Approach to Newborn Respiratory Care. 6th ed. Philidelpha, PA: Elsevier Academic Press, 2017.
-
- Partridge EA, Davey MG, Hornick MA, Flake AW: Pumpless Extracorporeal Support of the Preterm Infant: Bridging Fetal and Postnatal Physiology Neoreviews 18: e277–e282, 2017
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

