Central nervous system relapse in younger patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a LYSA and GLA/DSHNHL analysis
- PMID: 36716220
- PMCID: PMC10410133
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008888
Central nervous system relapse in younger patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a LYSA and GLA/DSHNHL analysis
Abstract
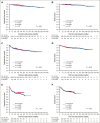
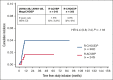
Most patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) can be cured with immunochemotherapy such as R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone). Patients with progression or relapse in the central nervous system (CNS) face dismal outcomes. The impact of more aggressive regimens used in frontline therapy has not been systematically investigated in this context. To this end, we analyzed a large cohort of 2203 younger patients with DLBCL treated on 10 German (German Lymphoma Alliance [GLA]/The German High Grade Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Study Group [DSHNHL]) and French (The Lymphoma Study Association [LYSA]) prospective phase 2 and 3 trials after first-line therapy with R-CHOP, R-CHOEP (R-CHOP + etoposide), dose-escalated R-CHOEP followed by repetitive stem cell transplantation (R-MegaCHOEP), or R-ACVBP (rituximab, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vindesine, bleomycine, and prednisone) followed by consolidation including multiple drugs crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Patients with DLBCL with an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index (aaIPI) of 0 to 1 showed very low cumulative incidence rates of CNS relapse regardless of first-line therapy and CNS prophylaxis (3-year cumulative incidences 0%-1%). Younger high-risk patients with aaIPI of 2 to 3 had 3-year cumulative incidence rates of 1.6% and 4% after R-ACVBP plus consolidation or R-(Mega)CHO(E)P, respectively (hazard ratio 2.4; 95% confidence interval: 0.8-7.4; P = .118). Thus, for younger high-risk patients, frontline regimens incorporating agents crossing the BBB may reduce often fatal CNS relapse.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.T. received honoraria from Roche, Amgen, Janssen, Celgene, and Gilead Science/Kyte Beigene; is in a consulting/advisory role for Roche, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Celgene, Novartis, BeiGene, and Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS)/Celgene; and received research funding, travel, and accommodations expenses from Roche and Novartis outside the submitted work. C.R. received research grants from AbbVie, Amgen, Novartis, BMS-Celgene, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Agios, Chugai, MaaT Pharma, Astellas, Roche, Daiichi-Sankyo, and IQVIA, and is an adviser for AbbVie, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Celgene, Otsuka, Astellas, Daiichi-Sankyo, Macrogenics, Pfizer, Roche, Servier, and Takeda. V.P. received travel support from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Gilead, and Roche. O.S. received research funding from Roche, Takeda, and Gilead, and is on the advisory board of and received honoraria from Celgene, Roche, Takeda, Gilead, BMS, Merck, AbbVie, and Janssen outside the submitted work. F.M. received research funding from Roche, Takeda, and Gilead, and is on the advisory board of and received honoraria from Celgene, Roche, Takeda, Gilead, BMS, Merck, AbbVie, and Janssen outside the submitted work. H.T. is on the advisory board of and received honoraria from Roche. G.L. received research funding from AstraZeneca, Agios, Aquinox, Bayer, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Morphosys, Novartis, Roche, and Verastem, and received honoraria from ADC Therapeutics, AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Celgene, Constellation, Genmab, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Karyopharm, Miltenyi, Morphosys, NanoString, Novartis, and Roche. N.S. received research funding from Janssen and received honoraria from Riemser/Esteve, Takeda, Kite/Gilead, and Novartis outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Schmitz N, Zeynalova S, Nickelsen M, et al. CNS International Prognostic Index: a risk model for CNS relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(26):3150–3156. - PubMed
-
- Frontzek F, Ziepert M, Nickelsen M, et al. Rituximab plus high-dose chemotherapy (MegaCHOEP) or conventional chemotherapy (CHOEP-14) in young, high-risk patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma: 10-year follow-up of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(4):e267–e277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

