Simultaneous recoupling of chemical shift tensors of two nuclei by R-symmetry sequences
- PMID: 36716616
- PMCID: PMC10023370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2023.107382
Simultaneous recoupling of chemical shift tensors of two nuclei by R-symmetry sequences
Abstract
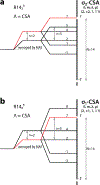
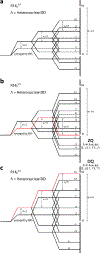
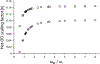
Chemical shift tensors (CSTs) are sensitive probes of structure and dynamics. R-symmetry pulse sequences (RNCSA) can efficiently recouple CSTs of varying magnitudes in magic angle spinning (MAS) NMR experiments, for a broad range of conditions and MAS frequencies. Herein, we introduce dual-channel R-symmetry pulse sequences for simultaneously recording CSTs of two different nuclei in a single experiment (DORNE-CSA). We demonstrate the performance of DORNE-CSA sequences for simultaneous measurement of 13C and 15N CSTs, on a U-13C,15N-labeled microcrystalline l-histidine. We show that the DORNE-CSA method is robust, provides accurate CST parameters, and takes only half of the measurement time compared to a pair of RNCSA experiments otherwise required for recording the CSTs of individual nuclei. DORNE-CSA approach is broadly applicable to a wide range of biological and inorganic systems.
Keywords: Chemical shift anisotropy; MAS NMR; R-symmetry; Simultaneous acquisition; Symmetry based recoupling.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recoupling of chemical shift anisotropy by R-symmetry sequences in magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy.J Chem Phys. 2012 Oct 7;137(13):134201. doi: 10.1063/1.4754149. J Chem Phys. 2012. PMID: 23039592 Free PMC article.
-
Composite-180° pulse-based symmetry sequences to recouple proton chemical shift anisotropy tensors under ultrafast MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy.J Magn Reson. 2015 Jan;250:45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 18. J Magn Reson. 2015. PMID: 25497846 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of accurate 19F chemical shift tensors with R-symmetry recoupling at high MAS frequencies (60-100 kHz).J Magn Reson. 2022 Jul;340:107227. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2022.107227. Epub 2022 Apr 26. J Magn Reson. 2022. PMID: 35568013 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in dipolar recoupling techniques under fast MAS in solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2021 Apr;112:101711. doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2020.101711. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 33508579 Review.
-
Measurement of proton chemical shift anisotropy in solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2018 Sep;93:16-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2018. PMID: 29803915 Review.
References
-
- Kupče Ē, Claridge TDW, NOAH: NMR Supersequences for Small Molecule Analysis and Structure Elucidation, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl, 56 (2017) 11779–11783. - PubMed
-
- Kupče Ē, Mote KR, Webb A, Madhu PK, Claridge TDW, Multiplexing Experiments in NMR and Multi-Nuclear MRI, Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc, 124–125 (2021) 1–56. - PubMed
-
- Gopinath T, Veglia G, Simultaneous Acquisition of Multiple Fast MAS Solid-State NMR Experiments Via Orphan Spin Polarization, in: Webb GA (Ed.) Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy, Academic Press, 2021, pp. 247–268.
-
- Kupče Ē, Frydman L, Webb AG, Yong JRJ, Claridge TDW, Parallel Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Nat. Rev. Methods Primers, 1 (2021) 27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

