Increasing Complexity of the N-Glycome During Caenorhabditis Development
- PMID: 36717059
- PMCID: PMC7614267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100505
Increasing Complexity of the N-Glycome During Caenorhabditis Development
Abstract
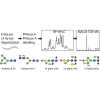
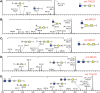
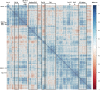
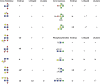
Caenorhabditis elegans is a frequently employed genetic model organism and has been the object of a wide range of developmental, genetic, proteomic, and glycomic studies. Here, using an off-line MALDI-TOF-MS approach, we have analyzed the N-glycans of mixed embryos and liquid- or plate-grown L4 larvae. Of the over 200 different annotatable N-glycan structures, variations between the stages as well as the mode of cultivation were observed. While the embryonal N-glycome appears less complicated overall, the liquid- and plate-grown larvae differ especially in terms of methylation of bisecting fucose, α-galactosylation of mannose, and di-β-galactosylation of core α1,6-fucose. Furthermore, we analyzed the O-glycans by LC-electrospray ionization-MS following β-elimination; especially the embryonal O-glycomes included a set of phosphorylcholine-modified structures, previously not shown to exist in nematodes. However, the set of glycan structures cannot be clearly correlated with levels of glycosyltransferase transcripts in developmental RNA-Seq datasets, but there is an indication for coordinated expression of clusters of potential glycosylation-relevant genes. Thus, there are still questions to be answered in terms of how and why a simple nematode synthesizes such a diverse glycome.
Keywords: fucose; galactose; glycomics; mass spectrometry; phosphorylcholine.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Haltiwanger R.S., Lowe J.B. Role of glycosylation in development. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004;73:491–537. - PubMed
-
- Smit C.H., van Diepen A., Nguyen D.L., Wuhrer M., Hoffmann K.F., Deelder A.M., et al. Glycomic analysis of life stages of the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni reveals developmental expression profiles of functional and antigenic glycan motifs. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2015;14:1750–1769. - PMC - PubMed
-
- C.-elegans-Sequencing-Consortium Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science. 1998;282:2012–2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

