Phenotypic CD8 T cell profiling in chronic hepatitis B to predict HBV-specific CD8 T cell susceptibility to functional restoration in vitro
- PMID: 36717219
- PMCID: PMC10579518
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327202
Phenotypic CD8 T cell profiling in chronic hepatitis B to predict HBV-specific CD8 T cell susceptibility to functional restoration in vitro
Abstract
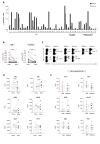
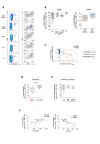
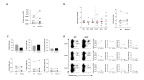
Objective: Exhausted hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific CD8 T cells in chronic HBV infection are broadly heterogeneous. Characterisation of their functional impairment may allow to distinguish patients with different capacity to control infection and reconstitute antiviral function.
Design: HBV dextramer+CD8 T cells were analysed ex vivo for coexpression of checkpoint/differentiation markers, transcription factors and cytokines in 35 patients with HLA-A2+chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and in 29 control HBsAg negative CHB patients who seroconverted after NUC treatment or spontaneously. Cytokine production was also evaluated in HBV peptide-stimulated T cell cultures, in the presence or absence of antioxidant, polyphenolic, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor and TLR-8 agonist compounds and the effect on HBV-specific responses was further validated on additional 24 HLA-A2 negative CHB patients.
Results: Severely exhausted HBV-specific CD8 T cell subsets with high expression of inhibitory receptors, such as PD-1, TOX and CD39, were detected only in a subgroup of chronic viraemic patients. Conversely, a large predominance of functionally more efficient HBV-specific CD8 T cell subsets with lower expression of coinhibitory molecules and better response to in vitro immune modulation, typically detected after resolution of infection, was also observed in a proportion of chronic viraemic HBV patients. Importantly, the same subset of patients who responded more efficiently to in vitro immune modulation identified by HBV-specific CD8 T cell analysis were also identified by staining total CD8 T cells with PD-1, TOX, CD127 and Bcl-2.
Conclusions: The possibility to distinguish patient cohorts with different capacity to respond to immune modulatory compounds in vitro by a simple analysis of the phenotypic CD8 T cell exhaustion profile deserves evaluation of its clinical applicability.
Keywords: T lymphocytes; cellular immunity; chronic viral hepatitis; immune response.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CF, Grant: Gilead, Abbvie. Consultant: Gilead, Abbvie, Vir Biotechnology, Arrowhead, Transgene, BMS; PL: advisor and speaker bureau for Gilead, Roche, BMS, GSK, MSD, Arrowhead, Alnylam, Spring Bank, Janssen, EIGER, Myr Pharma; AL: Consultant: MyrPharma, Gilead; MM: advisory board for Abbvie. SD, SPF, AG, JM, MG and LL are employees of and stock-holders in Gilead Sciences. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures





Comment in
-
Quest for immunological biomarkers in the management of CHB patients.Gut. 2023 Nov;72(11):2012-2014. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-329437. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Gut. 2023. PMID: 36922017 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
