A Phase 1 Trial of Durvalumab in Combination with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) or External Beam Radiation Therapy in Patients with BCG-unresponsive Non-muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: The Hoosier Cancer Research Network GU16-243 ADAPT-BLADDER Study
- PMID: 36717286
- PMCID: PMC10192088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.01.017
A Phase 1 Trial of Durvalumab in Combination with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) or External Beam Radiation Therapy in Patients with BCG-unresponsive Non-muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: The Hoosier Cancer Research Network GU16-243 ADAPT-BLADDER Study
Abstract
Background: Novel treatments and trial designs remain a high priority for bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG)-unresponsive non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) patients.
Objective: To evaluate the safety and preliminary efficacy of anti-PD-L1 directed therapy with durvalumab (D), durvalumab plus BCG (D + BCG), and durvalumab plus external beam radiation therapy (D + EBRT).
Design, setting, and participants: A multicenter phase 1 trial was conducted at community and academic sites.
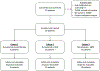
Intervention: Patients received 1120 mg of D intravenously every 3 wk for eight cycles. D + BCG patients also received full-dose intravesical BCG weekly for 6 wk with BCG maintenance recommended. D + EBRT patients received concurrent EBRT (6 Gy × 3 in cycle 1 only).
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Post-treatment cystoscopy and urine cytology were performed at 3 and 6 -mo, with bladder biopsies required at the 6-mo evaluation. The recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) for each regimen was the primary endpoint. Secondary endpoints included toxicity profiles and complete response (CR) rates.
Results and limitations: Twenty-eight patients were treated in the D (n = 3), D + BCG (n = 13), and D + EBRT (n = 12) cohorts. Full-dose D, full-dose BCG, and 6 Gy fractions × 3 were determined as the RP2Ds. One patient (4%) experienced a grade 3 dose limiting toxicity event of autoimmune hepatitis. The 3-mo CR occurred in 64% of all patients and in 33%, 85%, and 50% within the D, D + BCG, and D + EBRT cohorts, respectively. Twelve-month CRs were achieved in 46% of all patients and in 73% of D + BCG and 33% of D + EBRT patients.
Conclusions: D combined with intravesical BCG or EBRT proved feasible and safe in BCG-unresponsive NMIBC patients. Encouraging preliminary efficacy justifies further study of combination therapy approaches.
Patient summary: Durvalumab combination therapy can be safely administered to non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients with the goal of increasing durable response rates.
Keywords: Bacillus Calmette-Guerin; Bacillus Calmette-Guerin unresponsive; Bladder cancer; Clinical trial; Durvalumab; Non–muscle invasive; PD-L1; Radiation; Urothelial carcinoma.
Copyright © 2023 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
ADAPT and Improvise: Overcoming Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Unresponsiveness in Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer.Eur Urol. 2023 Jun;83(6):495-496. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.02.018. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Eur Urol. 2023. PMID: 36898871 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arends TJ, Nativ O, Maffezzini M, et al. Results of a randomised controlled trial comparing intravesical chemohyperthermia with mitomycin C versus bacillus Calmette-Guérin for adjuvant treatment of patients with intermediate- and high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2016;69:1046–52. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016. Eur Urol 2017;71:447–61. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute . Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program SEER*Stat Database: Incidence - SEER Research Data, 9 Registries, Nov 2020 Sub (1975–2018) - Linked To County Attributes - Time Dependent (1990–2018) Incom/Rurality, 1969–2019 Counties. April 2021. www.seer.cancer.gov2021
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

