Hepatocellular Damage and Severity of COVID-19 Infection in Iraqi Patients: A Biochemical Study
- PMID: 36718303
- PMCID: PMC9883029
- DOI: 10.52547/rbmb.11.3.524
Hepatocellular Damage and Severity of COVID-19 Infection in Iraqi Patients: A Biochemical Study
Abstract
Background: Infection with COVID-19 can cause hepatic damages. Here, we aimed to examine the effect of COVID-19 infection on the serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), albumin, and procalcitonin (PCT) concentrations as markers to evaluate the liver function.
Methods: In this study, 56 patients infected with COVID- 19 and 28 healthy controls was recruited in Private Nursing Home Hospital of the Medical City, Baghdad. Patients were subdivided according to disease severity into severe and non-severe groups.
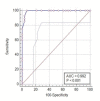
Results: The results showed that the mean±SD value of serum AST activity and serum PCT concentrations were elevated significantly in severe group in comparison to healthy control, (p< 0.01, p< 0.001) respectively. Also, the mean ±SD value of serum ALT activity was higher in severe group compared to the healthy subjects and non-severe ones, significantly (p< 0.0001, p< 0.003) respectively. While the mean value of serum albumin concentration of severe patients and non-severe group were significantly decreased compared to healthy subjects. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) revealed that ROC value of albumin (0.992) differentiates between non-severe infected patients and healthy subjects, while the ROC value of serum ALT activity (0.735) differentiates between severe COVID-19 patients and non- severe ones.
Conclusion: Changes of liver function parameters in COVID-19 patients were mild to moderate and measurement of serum ALT activity is the best biomarker in differentiation between non-severe patients and severe ones and albumin concentration is excellent in discrimination between patients and controls.
Keywords: Albumin; Procalcitonin; Serum aminotransferase enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The entire work had permitted by the Ethical Committees of local authorities. All participants provided an inscribed informed consent, and the research had conducted in line with the ethical morals identified in the 1975 treaty of Helsinki. The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest related to the present research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does Raised Transaminases Predict Severity and Mortality in Patients with COVID 19?J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 Jul-Aug;12(4):1114-1123. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Jan 31. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35125781 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocyte-C-reactive protein ratio can differentiate disease severity of COVID-19 patients and serve as an assistant screening tool for hospital and ICU admission.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 23;13:957407. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.957407. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36248811 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Indexes of Liver and Kidney Injury Markers Predict Severity in COVID-19 Patients.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Aug 10;14:3029-3040. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S321915. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34408447 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic monitoring of serum liver function indexes in patients with COVID-19.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Mar 6;9(7):1554-1562. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1554. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33728299 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the liver: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Hepatol Int. 2020 Sep;14(5):711-722. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10071-9. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Hepatol Int. 2020. PMID: 32623633 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Oxidative Stress Parameters in Iraqi Male Patients with Covid-19; A Case Control Study.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Jul;13(2):167-173. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.13.2.167. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39995639 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources