Synergistic Anti-Cancer Activity of the Combination of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and Retinoic Acid in U937 Cell Line
- PMID: 36718308
- PMCID: PMC9883028
- DOI: 10.52547/rbmb.11.3.440
Synergistic Anti-Cancer Activity of the Combination of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and Retinoic Acid in U937 Cell Line
Abstract
Background: MicroRNA is a form of non-coding RNAs that able to regulate gene expression. miR-424 is one of the members of the regulatory family, which plays an important role in the proliferation and differentiation of myeloid cells. Epigenetic changes can change the level of miR-424 under environmental factors. Therefore, the level of expression of miR-424 in U937 cells of the myeloid line was evaluated in this research under the influence of vitamin D3 (VitD3) and retinoic acid (RA).
Methods: In this study, U937 cells were cultured in the presence of VitD3, and RA to evaluate cell proliferation, viability via the trypan blue exclusion test, and expression level of miR-424 by real-time PCR at specific times.
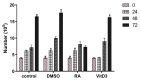
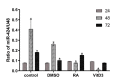
Results: Cell proliferation has shown a significant decrease in the RA group versus other groups during incubation times (P < 0.05). In VitD3 group, there was a significant increase in cell proliferation after 24- and 48-hours incubation periods versus other groups. In the VitD3 and RA groups, the increase of cell proliferation caused the downregulation of miR-424. In addition, the upregulation of VitD3 group and downregulation of the RA group were significant versus the control group (P < 0.05).
Discussion: We concluded that the expression level of miR-424 was critically affected in the dose- and time-dependent of RA and VitD3 treatment in the U937 cell line. Treatment with VitD3 decreased the expression of miR-424 and RA treatment increase miR-424 expression level in physiological doses.
Keywords: Cell Proliferation; Differentiation; U937 Cells; miR-424.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Natu Rev Gen. 2011;12:861–74. - PubMed
-
- Negrini M, Nicoloso MS, Calin GA. MicroRNAs and cancer—new paradigms in molecular oncology. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(3):470–9. - PubMed
-
- Medina PP, Nolde M, Slack FJ. OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 2010;467(7311):86–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
