Direct reconstruction for simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging based on multi-task learning
- PMID: 36719532
- PMCID: PMC9889598
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-023-00955-w
Direct reconstruction for simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging based on multi-task learning
Abstract
Background: Simultaneous dual-tracer positron emission tomography (PET) imaging can observe two molecular targets in a single scan, which is conducive to disease diagnosis and tracking. Since the signals emitted by different tracers are the same, it is crucial to separate each single tracer from the mixed signals. The current study proposed a novel deep learning-based method to reconstruct single-tracer activity distributions from the dual-tracer sinogram.
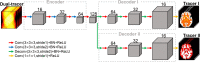
Methods: We proposed the Multi-task CNN, a three-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN) based on a framework of multi-task learning. One common encoder extracted features from the dual-tracer dynamic sinogram, followed by two distinct and parallel decoders which reconstructed the single-tracer dynamic images of two tracers separately. The model was evaluated by mean squared error (MSE), multiscale structural similarity (MS-SSIM) index and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) on simulated data and real animal data, and compared to the filtered back-projection method based on deep learning (FBP-CNN).
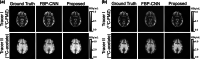
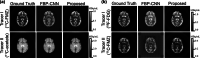
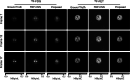
Results: In the simulation experiments, the Multi-task CNN reconstructed single-tracer images with lower MSE, higher MS-SSIM and PSNR than FBP-CNN, and was more robust to the changes in individual difference, tracer combination and scanning protocol. In the experiment of rats with an orthotopic xenograft glioma model, the Multi-task CNN reconstructions also showed higher qualities than FBP-CNN reconstructions.
Conclusions: The proposed Multi-task CNN could effectively reconstruct the dynamic activity images of two single tracers from the dual-tracer dynamic sinogram, which was potential in the direct reconstruction for real simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging data in future.
Keywords: Dual-tracer PET; Multi-task learning; Reconstruction; Signal separation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Signal separation of simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging based on global spatial information and channel attention.EJNMMI Phys. 2024 May 29;11(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40658-024-00649-9. EJNMMI Phys. 2024. PMID: 38809438 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based triple-tracer brain PET scanning in a single session: A simulation study using clinical data.Neuroimage. 2025 Jun;313:121246. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2025.121246. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Neuroimage. 2025. PMID: 40316225
-
Three-dimensional convolutional neural networks for simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging.Phys Med Biol. 2019 Sep 19;64(18):185016. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab3103. Phys Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31292287
-
Temporal information-guided dynamic dual-tracer PET signal separation network.Med Phys. 2022 Jul;49(7):4585-4598. doi: 10.1002/mp.15566. Epub 2022 May 23. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 35396705
-
CT artifact correction for sparse and truncated projection data using generative adversarial networks.Med Phys. 2021 Feb;48(2):615-626. doi: 10.1002/mp.14504. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 32996149 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learned triple-tracer multiplexed PET myocardial image separation.Front Nucl Med. 2024 Apr 11;4:1379647. doi: 10.3389/fnume.2024.1379647. eCollection 2024. Front Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 39381030 Free PMC article.
-
Expert consensus on workflow of PET/CT with long axial field-of-view.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Feb;52(3):1038-1049. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06968-4. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39520515 Review.
-
Signal separation of simultaneous dual-tracer PET imaging based on global spatial information and channel attention.EJNMMI Phys. 2024 May 29;11(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40658-024-00649-9. EJNMMI Phys. 2024. PMID: 38809438 Free PMC article.
-
AI for PET image reconstruction.Br J Radiol. 2023 Oct;96(1150):20230292. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20230292. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37486607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning-based PET image denoising and reconstruction: a review.Radiol Phys Technol. 2024 Mar;17(1):24-46. doi: 10.1007/s12194-024-00780-3. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Radiol Phys Technol. 2024. PMID: 38319563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang SC, Carson RE, Hoffman EJ, Kuhl DE, Phelps ME. An investigation of a double-tracer technique for positron computerized tomography. J Nucl Med. 1982;23(9):816–22. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

