Separation of Isomeric Forms of Urolithin Glucuronides Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
- PMID: 36719954
- PMCID: PMC9936581
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07145
Separation of Isomeric Forms of Urolithin Glucuronides Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
Abstract
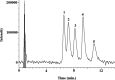
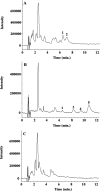
Urolithins are gut microbiota metabolites produced in humans after consuming foods containing ellagitannins and ellagic acid. Three urolithin metabotypes have been reported for different individuals depending on the final urolithins produced. After absorption, they are conjugated with glucuronic acid (phase II metabolism), and these are the main circulating metabolites in plasma and reach different tissues. Different regioisomeric isomers of urolithin glucuronides have been described. Still, their identification and quantification in humans have not been properly reported due to resolution limitations in their analysis by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. In the present study, we report a novel method for separating these isomers using supercritical fluid chromatography. With this method, urolithin A 3- and 8-glucuronide, isourolithin A 3- and 9- glucuronide, and urolithin B 3-glucuronide (8-hydroxy urolithin 3-glucuronide; 3-hydroxy urolithin 8-glucuronide; 3-hydroxyurolithin 9-glucuronide; 9-hydroxyurolithin 3-glucuronide; and urolithin 3-glucuronide) were separated in less than 15 min. The proposed method was applied to successfully analyze these metabolites in urine samples from different volunteers belonging to different metabotypes.
Keywords: chromatographic separation; glucuronides; gut microbiota metabolites; supercritical fluid chromatography; urolithins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Landete J. M. Ellagitannins, ellagic acid and their derived metabolites: a review about source, metabolism, functions and health. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1150–1160. 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.04.027. - DOI
-
- González-Sarrías A.; García-Villalba R.; Núñez-Sánchez M. A.; Tomé-Carneiro J.; Zafrilla P.; Mulero J.; Tomás-Barberán F. A.; Espín J. C. Identifying the limits for ellagic acid bioavailability: A crossover pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers after consumption of pomegranate extracts. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 225–235. 10.1016/j.jff.2015.09.019. - DOI
-
- González-Sarrías A.; Espín J. C.; Tomás-Barberán F. A. Non-extractable polyphenols produce gut microbiota metabolites that persist in circulation and show anti-inflammatory and free radical-scavenging effects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 281–288. 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.07.010. - DOI
-
- García-Villalba R.; Gimenez-Bastida J. A.; Cortes-Martin A.; Avila-Galvez M. A.; Tomas-Barberan F. A.; Selma M. V.; Espin J. C.; Gonzalez-Sarrias A. Urolithins: a comprehensive update on their metabolism, bioactivity, and associated gut microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2101019.10.1002/mnfr.202101019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

