Adjuvant Osimertinib for Resected EGFR-Mutated Stage IB-IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results From the Phase III Randomized ADAURA Trial
- PMID: 36720083
- PMCID: PMC10082285
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.02186
Adjuvant Osimertinib for Resected EGFR-Mutated Stage IB-IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results From the Phase III Randomized ADAURA Trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Adjuvant Osimertinib for Resected EGFR-Mutated Stage IB-IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results From the Phase III Randomized ADAURA Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Aug 1;41(22):3877. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00658. Epub 2023 Apr 27. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37104731 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
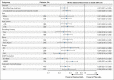
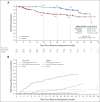
Purpose: The phase III ADAURA (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02511106) primary analysis demonstrated a clinically significant disease-free survival (DFS) benefit with adjuvant osimertinib versus placebo in EGFR-mutated stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after complete tumor resection (DFS hazard ratio [HR], 0.20 [99.12% CI, 0.14 to 0.30]; P < .001). We report an updated exploratory analysis of final DFS data.
Methods: Overall, 682 patients with stage IB-IIIA (American Joint Committee on Cancer/Union for International Cancer Control, seventh edition) EGFR-mutated (exon 19 deletion/L858R) NSCLC were randomly assigned 1:1 (stratified by stage, mutational status, and race) to receive osimertinib 80 mg once-daily or placebo for 3 years. The primary end point was DFS by investigator assessment in stage II-IIIA disease analyzed by stratified log-rank test; following early reporting of statistical significance in DFS, no further formal statistical testing was planned. Secondary end points included DFS in stage IB-IIIA, overall survival, and safety. Patterns of recurrence and CNS DFS were prespecified exploratory end points.
Results: At data cutoff (April 11, 2022), in stage II-IIIA disease, median follow-up was 44.2 months (osimertinib) and 19.6 months (placebo); the DFS HR was 0.23 (95% CI, 0.18 to 0.30); 4-year DFS rate was 70% (osimertinib) and 29% (placebo). In the overall population, DFS HR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.21 to 0.34); 4-year DFS rate was 73% (osimertinib) and 38% (placebo). Fewer patients treated with osimertinib had local/regional and distant recurrence versus placebo. CNS DFS HR in stage II-IIIA was 0.24 (95% CI, 0.14 to 0.42). The long-term safety profile of osimertinib was consistent with the primary analysis.
Conclusion: These updated data demonstrate prolonged DFS benefit over placebo, reduced risk of local and distant recurrence, improved CNS DFS, and a consistent safety profile, supporting the efficacy of adjuvant osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Improving Report of the ADAURA Trial by Distinguishing Treatment-Related Adverse Events From Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events and Assessing Independence of Censoring in Final Disease-Free Survival Analyses.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep 10;41(26):4317-4318. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00604. Epub 2023 Jun 30. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37390376 No abstract available.
-
ADAURA update: only the end of the beginning.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 31;12(7):1649-1651. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-237. Epub 2023 May 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37577316 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Adoring ADAURA: can we cure lung cancer that harbors an EGFR mutation?Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 31;12(7):1625-1627. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-222. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37577323 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Adjuvant osimertinib for resected EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: a game-changer?Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 31;12(7):1631-1635. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-273. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37577327 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kris MG, Gaspar LE, Chaft JE, et al. : Adjuvant systemic therapy and adjuvant radiation therapy for stage I to IIIA completely resected non-small-cell lung cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology/Cancer Care Ontario clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 35:2960-2974, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Pisters K, Kris MG, Gaspar LE, et al. : Adjuvant systemic therapy and adjuvant radiation therapy for stage I-IIIA completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer: ASCO guideline rapid recommendation update. J Clin Oncol 40:1127-1129, 2022 - PubMed
-
- Postmus PE, Kerr KM, Oudkerk M, et al. : Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 28:iv1-iv21, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Remon J, Soria JC, Peters S, et al. : Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: An update of the ESMO clinical practice guidelines focusing on diagnosis, staging, systemic and local therapy. Ann Oncol 32:1637-1642, 2021 - PubMed
-
- Pignon JP, Tribodet H, Scagliotti GV, et al. : Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: A pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. J Clin Oncol 26:3552-3559, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

