Is tranexamic acid associated with decreased need for blood transfusion in percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36720263
- PMCID: PMC9889173
- DOI: 10.1308/rcsann.2021.0259
Is tranexamic acid associated with decreased need for blood transfusion in percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Bleeding is a common complication after percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL) for renal stone disease. Tranexamic acid (TXA) has been found to reduce mortality and blood transfusion in surgical and trauma patients. This review aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of TXA in patients undergoing PNL.
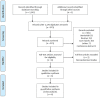
Methods: A systematic literature review was performed to recognise all randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the use of TXA in PNL. The primary outcome of the study was to compare the need for blood transfusion with and without TXA.
Findings: Six RCTs with 1,323 patients were included in this review. Haemoglobin fall was lower in the TXA group compared with the control group, and the need for blood transfusion was reduced by 67% (odds ratio (OR) 0.33, confidence interval (CI) (0.21, 0.52), p<0.00001). However, blood loss was comparable for the two groups (mean difference -116.9, CI (-244.5,10.7) p=0.07). Length of stay and duration of surgery was significantly shorter with TXA. Furthermore, both minor and major complications were lower in the TXA group. Stone-free rate was higher with the TXA group. No thromboembolic complications were noted in the TXA group.
Conclusions: TXA is safe and efficacious for PNL with a reduction in need for blood transfusion and without an attending increase in complication rates.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Percutaneous nephrolithotomy; Tranexamic acid.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antifibrinolytics for heavy menstrual bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 15;4(4):CD000249. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000249.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29656433 Free PMC article.
-
Antifibrinolytic drugs for treating primary postpartum haemorrhage.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 20;2(2):CD012964. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012964. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29462500 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of oral tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 May;97(18):e0587. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010587. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29718858 Free PMC article.
-
Mini Versus Standard Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for the Management of Renal Stone Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Eur Urol Focus. 2022 Sep;8(5):1376-1385. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.07.014. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Eur Urol Focus. 2022. PMID: 34404619
-
Peri-articular administration of tranexamic acid is an alternative route in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Apr 7;17(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03095-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35392961 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tranexamic acid for percutaneous nephrolithotomy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 26;10(10):CD015122. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015122.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37882229 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic vs. in-irrigation tranexamic acid in percutaneous nephrolithotomy A systematic review, Bayesian network meta-analysis, and meta-regression.Can Urol Assoc J. 2024 Sep;18(9):E285-E290. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.8721. Can Urol Assoc J. 2024. PMID: 39190177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Tranexamic Acid (TXA) on Postoperative Bleeding in Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Obes Surg. 2025 Apr;35(4):1504-1512. doi: 10.1007/s11695-025-07709-8. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Obes Surg. 2025. PMID: 40072741
References
-
- Kessaris DN, Bellman GC, Pardalidis NPet al. Management of hemorrhage after percutaneous renal surgery. J Urol 1995; 153: 604–608. - PubMed
-
- Myles PS, Smith JA, Forbes Aet al. Tranexamic acid in patients undergoing coronary-artery surgery. N Engl J Med 2017; 376: 136–148. - PubMed
-
- de Vasconcellos SJ, de Santana Santos T, Reinheimer DMet al. Topical application of tranexamic acid in anticoagulated patients undergoing minor oral surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017; 45: 20–26. - PubMed
-
- Fillingham YA, Ramkumar DB, Jevsevar DSet al. The efficacy of tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: a network meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty 2018; 33: 3083–3089.e4. - PubMed
-
- Morrison JJ, Dubose JJ, Rasmussen TEet al. Military application of tranexamic acid in trauma emergency resuscitation (MATTERs) study. Arch Surg 2012; 147: 113–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

