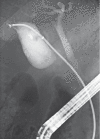
Introducer-assisted endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder biopsy for indeterminate gallbladder fundal wall thickness
- PMID: 36720267
- PMCID: PMC9889165
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1996-0604
Introducer-assisted endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder biopsy for indeterminate gallbladder fundal wall thickness
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nagino M, Hirano S, Yoshitomi H et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of biliary tract cancers 2019: The 3rd English edition. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2021;28:26–54. - PubMed
-
- Pouw R E, Barret M, Biermann K et al. Endoscopic tissue sampling – Part 1: Upper gastrointestinal and hepatopancreatobiliary tracts. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy. 2021;53:1174–1188. - PubMed
-
- Kito Y, Kato A, Yoshida M et al. Facile and secure deployment of plastic stent through an endoscopic tapered sheath for endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage. Endoscopy. 2022;54:E674–E675. - PubMed
-
- Kamada H, Kobara H, Yamana H et al. Endoscopic direct visualization of gallbladder polypoid lesion using peroral digital single-operator cholangioscopy. Endoscopy. 2021;53:E263–E264. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

