Nanotechnology-enabled immunogenic cell death for improved cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 36720448
- PMCID: PMC9975075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122655
Nanotechnology-enabled immunogenic cell death for improved cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
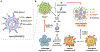
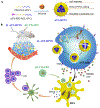
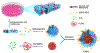
Tumor immunotherapy has revolutionized the field of oncology treatments in recent years. As one of the promising strategies of cancer immunotherapy, tumor immunogenic cell death (ICD) has shown significant potential for tumor therapy. Nanoparticles are widely used for drug delivery due to their versatile characteristics, such as stability, slow blood elimination, and tumor-targeting ability. To increase the specificity of ICD inducers and improve the efficiency of ICD induction, functionally specific nanoparticles, such as liposomes, nanostructured lipid carriers, micelles, nanodiscs, biomembrane-coated nanoparticles and inorganic nanoparticles have been widely reported as the vehicles to deliver ICD inducers in vivo. In this review, we summarized the strategies of different nanoparticles for ICD-induced cancer immunotherapy, and systematically discussed their advantages and disadvantages as well as provided feasible strategies for solving these problems. We believe that this review will offer some insights into the design of effective nanoparticulate systems for the therapeutic delivery of ICD inducers, thus, promoting the development of ICD-mediated cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Nanoparticles; Tumor immunogenic cell death; Tumor immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Promotion of ICD via Nanotechnology.Macromol Biosci. 2023 Sep;23(9):e2300093. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202300093. Epub 2023 May 7. Macromol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37114599 Review.
-
Bioactive Peptide Nanodrugs Based on Supramolecular Assembly for Boosting Immunogenic Cell Death-Induced Cancer Immunotherapy.Small Methods. 2023 May;7(5):e2201708. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202201708. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Small Methods. 2023. PMID: 36720041 Review.
-
Rediscovery of nanoparticle-based therapeutics: boosting immunogenic cell death for potential application in cancer immunotherapy.J Mater Chem B. 2021 May 19;9(19):3983-4001. doi: 10.1039/d1tb00397f. J Mater Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33909000 Review.
-
Nano Delivery of Chemotherapeutic ICD Inducers for Tumor Immunotherapy.Small Methods. 2023 May;7(5):e2201307. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202201307. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Small Methods. 2023. PMID: 36604976 Review.
-
Stimuli-responsive nanodelivery systems for amplifying immunogenic cell death in cancer immunotherapy.Immunol Rev. 2024 Jan;321(1):181-198. doi: 10.1111/imr.13237. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37403660 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology-Based Strategies for Safe and Effective Immunotherapy.Molecules. 2024 Dec 11;29(24):5855. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245855. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39769944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-based nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy.Med Rev (2021). 2023 Aug 17;3(3):230-269. doi: 10.1515/mr-2023-0020. eCollection 2023 Jun. Med Rev (2021). 2023. PMID: 37789955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocarriers for cutting-edge cancer immunotherapies.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 16;23(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06435-0. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40234928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing immunotherapy with tumour-responsive nanomaterials.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2025 Apr;22(4):262-282. doi: 10.1038/s41571-025-01000-6. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40050505 Review.
-
The evolution of immune profiling: will there be a role for nanoparticles?Nanoscale Horiz. 2024 Oct 21;9(11):1896-1924. doi: 10.1039/d4nh00279b. Nanoscale Horiz. 2024. PMID: 39254004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbas Z and Rehman S, An overview of cancer treatment modalities. Neoplasm, 2018. 1: p. 139–157.
-
- Waks AG and Winer EP, Breast cancer treatment: a review. Jama, 2019. 321(3): p. 288–300. - PubMed
-
- Lepeltier E, et al., Nanomedicine to target multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resistance Updates, 2020. 52: p. 100704. - PubMed
-
- Engle K and Kumar G, Cancer multidrug-resistance reversal by ABCB1 inhibition: A recent update. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2022: p. 114542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

