Linear ubiquitination induces NEMO phase separation to activate NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 36720498
- PMCID: PMC9889916
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202201607
Linear ubiquitination induces NEMO phase separation to activate NF-κB signaling
Abstract
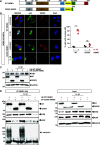
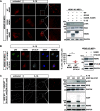
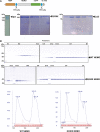
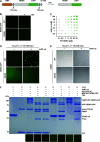
The NF-κB essential modulator NEMO is the core regulatory component of the inhibitor of κB kinase complex, which is a critical checkpoint in canonical NF-κB signaling downstream of innate and adaptive immune receptors. In response to various stimuli, such as TNF or IL-1β, NEMO binds to linear or M1-linked ubiquitin chains generated by LUBAC, promoting its oligomerization and subsequent activation of the associated kinases. Here we show that M1-ubiquitin chains induce phase separation of NEMO and the formation of NEMO assemblies in cells after exposure to IL-1β. Phase separation is promoted by both binding of NEMO to linear ubiquitin chains and covalent linkage of M1-ubiquitin to NEMO and is essential but not sufficient for its phase separation. Supporting the functional relevance of NEMO phase separation in signaling, a pathogenic NEMO mutant, which is impaired in both binding and linkage to linear ubiquitin chains, does not undergo phase separation and is defective in mediating IL-1β-induced NF-κB activation.
© 2023 Goel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
