Survival by Depth of Response and Efficacy by International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium Subgroup with Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Analysis of the Phase 3 Randomized CLEAR Study
- PMID: 36720658
- PMCID: PMC10875602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.01.010
Survival by Depth of Response and Efficacy by International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium Subgroup with Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Analysis of the Phase 3 Randomized CLEAR Study
Abstract
Background: The extent of tumor shrinkage has been deemed a predictor of survival for advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC), a disease with historically poor survival.
Objective: To perform an exploratory analysis of overall survival (OS) by tumor response by 6 mo, and to assess the efficacy and survival outcomes in specific subgroups.
Design, setting, and participants: CLEAR was an open-label, multicenter, randomized, phase 3 trial of first-line treatment of advanced clear cell RCC.
Intervention: Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to lenvatinib 20 mg orally daily with pembrolizumab 200 mg intravenously once every 3 wk, lenvatinib plus everolimus (not included in this analysis), or sunitinib 50 mg orally daily for 4 wk on treatment/2 wk of no treatment.
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Landmark analyses were conducted to assess the association of OS with tumor shrinkage and progressive disease status by 6 mo. Progression-free survival, duration of response, and objective response rate (ORR) were analyzed by the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) risk subgroup and by the presence of target kidney lesions. Efficacy was assessed by an independent review committee as per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1.
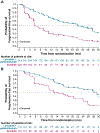
Results and limitations: Landmark analyses by tumor shrinkage showed that patients enrolled to lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab arm with a confirmed complete response or >75% target-lesion reduction by 6 mo had a 24-mo OS probability of ≥91.7%. A landmark analysis by disease progression showed that patients with no progression by 6 mo had lower probabilities of death in both arms. Patients with an IMDC risk classification of intermediate/poor had longer median progression-free survival (22.1 vs 5.9 mo) and a higher ORR (72.4% vs 28.8%) with lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus sunitinib. Similarly, results favored lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in IMDC-favorable patients and those with/without target kidney lesions. Limitations of the study are that results were exploratory and not powered/stratified.
Conclusions: Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab showed improved efficacy versus sunitinib for patients with advanced RCC; landmark analyses showed that tumor response by 6 mo correlated with longer OS.
Patient summary: In this report of the CLEAR trial, we explored the survival of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma by assessing how well they initially responded to treatment. We also explored how certain groups of patients responded to treatment overall. Patients were assigned to cycles of either lenvatinib 20 mg daily plus pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 wk or sunitinib 50 mg daily for 4 wk (followed by a 2-wk break). Patients who either had a "complete response" or had their tumors shrunk by >75% within 6 mo after starting treatment with lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab had better survival than those with less tumor reduction by 6 mo. Additionally, patients who had more severe disease (as per the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium) at the start of study treatment survived for longer without disease progression with lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab than with sunitinib.
Keywords: Depth of response; Lenvatinib; Pembrolizumab; Renal cell carcinoma; Sunitinib.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
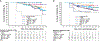

References
-
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER). Cancer stat facts: kidney and renal pelvis cancer https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html.
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). GLOBOCAN 2020. Cancer Today. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2017;376:354–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

