TRPV1 regulates ApoE4-disrupted intracellular lipid homeostasis and decreases synaptic phagocytosis by microglia
- PMID: 36720919
- PMCID: PMC9981624
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-023-00935-z
TRPV1 regulates ApoE4-disrupted intracellular lipid homeostasis and decreases synaptic phagocytosis by microglia
Abstract
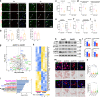
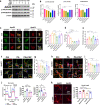
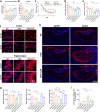
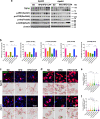
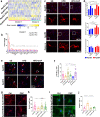
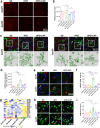
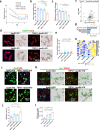
Although the ε4 allele of the apolipoprotein E (ApoE4) gene has been established as a genetic risk factor for many neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, the mechanism of action remains poorly understood. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) was reported to regulate autophagy to protect against foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Here, we show that ApoE4 leads to lipid metabolism dysregulation in microglia, resulting in enhanced MHC-II-dependent antigen presentation and T-cell activation. Lipid accumulation and inflammatory reactions were accelerated in microglia isolated from TRPV1flox/flox; Cx3cr1cre-ApoE4 mice. We showed that metabolic boosting by treatment with the TRPV1 agonist capsaicin rescued lipid metabolic impairments in ApoE4 neurons and defects in autophagy caused by disruption of the AKT-mTOR pathway. TRPV1 activation with capsaicin reversed ApoE4-induced microglial immune dysfunction and neuronal autophagy impairment. Capsaicin rescued memory impairment, tau pathology, and neuronal autophagy in ApoE4 mice. Activation of TRPV1 decreased microglial phagocytosis of synapses in ApoE4 mice. TRPV1 gene deficiency exacerbated recognition memory impairment and tau pathology in ApoE4 mice. Our study suggests that TRPV1 regulation of lipid metabolism could be a therapeutic approach to alleviate the consequences of the ApoE4 allele.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

