The influence of individual, peer, and family factors on the educational aspirations of adolescents in rural China
- PMID: 36721824
- PMCID: PMC9880925
- DOI: 10.1007/s11218-023-09765-3
The influence of individual, peer, and family factors on the educational aspirations of adolescents in rural China
Abstract
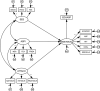
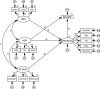
Educational aspirations are an important predictor of academic outcomes. While there has been considerable research on educational aspirations in the West, there has been little research in East Asia, and the investigation of factors influencing adolescent aspirations has been neglected, particularly in rural areas. Drawing on ecological systems theory and social cognitive career theory, this study investigated the associations between educational aspirations and factors at the individual, peer, and family levels among rural Chinese adolescents. A total of 606 students (M age = 14.85 years; 50% boys) from a rural town in Central China completed questionnaires assessing their educational aspirations, individual factors (academic performance, academic self-perception, academic self-regulation, attitudes toward teachers, and goal valuation), and contextual factors (family socioeconomic status, parent and peer relationship quality, and parental and close friends' aspirations). Individual factors and aspirations of others had significant direct effects on adolescents' educational aspirations, while parent and peer attachments were significantly related to educational aspirations via individual factors. Family socioeconomic status was not significantly related to adolescents' educational aspirations. The findings highlight the importance of individual factors as mechanisms explaining the link between contextual factors and rural Chinese adolescents' educational aspirations. Our results suggest that interventions can be designed to increase and maintain the aspirations of rural Chinese youth by targeting multiple domains of influence.
Keywords: China; Educational aspirations; Parent–child relationship; Peer relationships; Rural adolescents.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestNo funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Arbuckle, J. L. (2012). Amos (Version 21.0) [Computer Program]. Chicago: IBM SPSS.
-
- Bagozzi RP, Yi YJ. On the use of structural equation models in experimental-designs. Journal of Marketing Research. 1989;26(3):271–284. doi: 10.1177/002224378902600302. - DOI
-
- Bandura A. Social learning theory. Prentice Hall; 1976.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
