An audit of cancellation of elective surgery in paediatric patients at Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital
- PMID: 36722562
- PMCID: PMC10117019
- DOI: 10.4103/ajps.ajps_111_21
An audit of cancellation of elective surgery in paediatric patients at Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital
Abstract
Background: Cancellation of elective surgery is one of the quality indicators of theatre operation worldwide. The cancellation of elective surgery in paediatric patients is a worldwide problem with the rates ranging from 0.21% to 44%. This study aimed to determine the rates and describe the reasons for cancellation of elective surgeries in paediatric patients at Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital (CHBAH).
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was conducted using theatre records from 1st January to 31st December 2019. The numbers and reasons for elective paediatric surgeries were reviewed. Data were collected using the structured collection sheet and entered into Microsoft Excel. Statistical Package for the Social Sciences was also used to further analyse the data. Results were expressed as percentages in a graph and table forms.
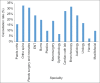
Results: In the year 2019, a total of 3399 elective paediatric procedures were scheduled in 14 specialities at CHBAH. Of these, 634 (19%) were cancelled due to various reasons. The highest number of cases cancelled were from paediatric surgery and neonates (n = 204, 31%), followed by ear nose and throat (n = 99, 24%), burns (n = 80, 20%) and paediatric orthopaedics (n = 79, 16%). The most common reason for cancellation of elective surgery in paediatric patients at CHBAH was found to be time constraint (34%). The reasons for cancellation in our study were mostly due to avoidable factors at 68% and non-avoidable at 32%.
Conclusion: The rate of cancellation in our study was high. Majority of the causes for cancellation were avoidable.
Keywords: Cancellation; elective surgery; paediatric; theatre efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancellation of elective surgical cases in a nigerian teaching hospital: Frequency and reasons.Niger J Clin Pract. 2020 Jul;23(7):965-969. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_650_19. Niger J Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32620726
-
Prevalence and factors associated with cancellation and deferment of elective surgical cases at a rural private tertiary hospital in Western Uganda: a cross-sectional study.Pan Afr Med J. 2021 Jun 17;39:139. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.39.139.24667. eCollection 2021. Pan Afr Med J. 2021. PMID: 34527155 Free PMC article.
-
Reasons for cancellation of operation on the day of intended surgery in a multidisciplinary 500 bedded hospital.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;28(1):66-9. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.92442. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22345949 Free PMC article.
-
Cancellation of Surgeries: Integrative Review.J Perianesth Nurs. 2019 Feb;34(1):86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jopan.2017.09.012. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Perianesth Nurs. 2019. PMID: 29678319 Review.
-
Evaluating factors associated with the cancellation and delay of elective surgical procedures: a systematic review.Int J Qual Health Care. 2021 Jun 26;33(2):mzab092. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzab092. Int J Qual Health Care. 2021. PMID: 34100548
Cited by
-
Model proposal for calculating waste associated with processing consigned surgical instruments.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2023 Dec 4;31:e4061. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.6716.4061. eCollection 2023. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2023. PMID: 38055587 Free PMC article.
-
The Social Challenges of Stomas Faced by Families of Children With Anorectal Malformations in Uganda.Sage Open Pediatr. 2025 May 29;12:30502225251338534. doi: 10.1177/30502225251338534. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Sage Open Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40612179 Free PMC article.
-
Methods families use to raise funds for anorectal malformation treatment at a single public referral hospital in Southwestern Uganda.World J Pediatr Surg. 2024 Dec 24;7(4):e000877. doi: 10.1136/wjps-2024-000877. eCollection 2024. World J Pediatr Surg. 2024. PMID: 39737079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huda F. A Retrospective analysis of reasons for cancellation of elective surgery in a teaching hospital. Int J Sci Stud. 2014;2:28–30.
-
- Tait AR, Voepel-Lewis T, Munro HM, Gutstein HB, Reynolds PI. Cancellation of pediatric outpatient surgery: Economic and emotional implications for patients and their families. J Clin Anesth. 1997;9:213–9. - PubMed
-
- Chiu CH, Lee A, Chui PT. Cancellation of elective operations on the day of intended surgery in a Hong Kong hospital: Point prevalence and reasons. Hong Kong Med J. 2012;18:5–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical