Bridging the gap: leveraging implementation science to advance pediatric behavioral sleep interventions
- PMID: 36722616
- PMCID: PMC10315605
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.10476
Bridging the gap: leveraging implementation science to advance pediatric behavioral sleep interventions
Abstract
Study objectives: This review synthesizes the pediatric behavioral sleep intervention (BSI) evidence base, summarizes challenges in translating BSIs from research to practice, and provides recommendations for integrating implementation science methods to advance pediatric BSI research.
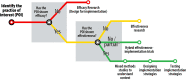
Methods: We briefly review the common behavioral sleep disturbances among youth, discuss the pediatric BSIs with well-established evidence, and identify gaps in pediatric BSI research. We then identify contributors to the dearth of research evaluating pediatric BSIs in accessible settings and present a model for applying implementation science strategies to address identified gaps across the continuum of translational research.
Results: Relatively few BSI trials include older children and adolescents. Similarly, there is limited research evaluating BSIs among racially and ethnically minoritized children and families and/or those of lower socioeconomic status backgrounds. Access to scalable and easily disseminable tools to treat pediatric sleep disturbances early in their development is crucial for promoting positive child outcomes. To address these gaps, researchers should apply implementation science theories, models, and frameworks to design new interventions for implementation, adapt existing interventions with end users and settings in mind, conduct hybrid effectiveness-implementation trials, and test implementation strategies.
Conclusions: Given the prevalence and consequences of poor sleep across developmental periods, pediatric BSIs must be effective as well as adaptable, scalable, and easily disseminable. Implementation science theories, models, and frameworks can enhance access to, engagement in, and the implementation and dissemination of scalable BSIs across diverse pediatric care settings and heterogeneous populations.
Citation: Levenson JC, Williamson AA. Bridging the gap: leveraging implementation science to advance pediatric behavioral sleep interventions. J Clin Sleep Med. 2023;19(7):1321-1336.
Keywords: adolescence; behavioral; childhood; dissemination; effectiveness; implementation; intervention; minoritized; pediatrics.
© 2023 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have seen and approved this manuscript. Work for this study was performed at the University of Pittsburgh, University of Pennsylvania, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. This work was supported by Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) grant K23HD087433 (J.C.L.) and NICHD grant K23HD094905. Dr. Levenson receives royalties from American Psychological Association Books. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mindell JA , Owens JA . A Clinical Guide to Pediatric Sleep: Diagnosis and Management of Sleep Problems. Philadelphia: : Wolters Kluwer; ; 2015. .
-
- Matricciani L , Paquet C , Galland B , Short M , Olds T . Children’s sleep and health: a meta-review . Sleep Med Rev. 2019. ; 46 : 136 – 150 . - PubMed
-
- Meltzer LJ , Mindell JA . Systematic review and meta-analysis of behavioral interventions for pediatric insomnia . J Pediatr Psychol. 2014. ; 39 ( 8 ): 932 – 948 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

