Effective bridging therapy can improve CD19 CAR-T outcomes while maintaining safety in patients with large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 36724512
- PMCID: PMC10300297
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009019
Effective bridging therapy can improve CD19 CAR-T outcomes while maintaining safety in patients with large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
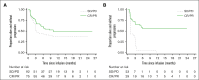
The impact of bridging therapy (BT) on CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CD19CAR-T) outcomes in large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) is poorly characterized. Current practice is guided through physician preference rather than established evidence. Identification of effective BT modalities and factors predictive of response could improve both CAR-T intention to treat and clinical outcomes. We assessed BT modality and response in 375 adult patients with LBCL in relation to outcomes after axicabtagene ciloleucel (Axi-cel) or tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-cel) administration. The majority of patients received BT with chemotherapy (57%) or radiotherapy (17%). We observed that BT was safe for patients, with minimal morbidity or mortality. We showed that complete or partial response to BT conferred a 42% reduction in disease progression and death after CD19CAR-T therapy. Multivariate analysis identified several factors associated with likelihood of response to BT, including response to last line therapy, the absence of bulky disease, and the use of polatuzumab-containing chemotherapy regimens. Our data suggested that complete or partial response to BT may be more important for Tisa-cel than for Axi-cel, because all patients receiving Tisa-cel with less than partial response to BT experienced frank relapse within 12 months of CD19CAR-T infusion. In summary, BT in LBCL should be carefully planned toward optimal response and disease debulking, to improve patient outcomes associated with CD19CAR-T. Polatuzumab-containing regimens should be strongly considered for all suitable patients, and failure to achieve complete or partial response to BT before Tisa-cel administration may prompt consideration of further lines of BT where possible.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.K., S.C., C.B, S.I., and C.R. have served on advisory boards and received honoraria from Kite/Gilead, Novartis, and Bristol Myers Squibb. A.A.K. received honoraria from Kite/Gilead. R.S., D.I., B.U., E.T., C.J., and M.O. have served on advisory boards and received honoraria from Kite/Gilead and Novartis. W.O. has served on advisory boards and received honoraria from Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Roche, Servier, and Pfizer. W.T. has received honoraria and consultancy fees from Kite, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Roche. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kuhnl A, Roddie C, Kirkwood AA, et al. A national service for delivering CD19 CAR-T in large B-cell lymphoma - The UK real-world experience. Br J Haematol. 2022;198(3):492–502. - PubMed
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45–56. - PubMed
-
- Nastoupil LJ, Jain MD, Spiegel JY, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel (Axi-cel) CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma: real world experience. Blood. 2018;132(Supplement 1) 91-91.
-
- Jaglowski S, Hu ZH, Zhang Y, et al. Tisagenlecleucel chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) t-cell therapy for adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): real world experience from the center for international blood & marrow transplant research (CIBMTR) cellular therapy (CT) Registry. Blood. 2019;134(Supplement_1) 766-766.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

