Hyperammonemia Due to Empyema
- PMID: 36725045
- PMCID: PMC10518550
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0922-22
Hyperammonemia Due to Empyema
Abstract
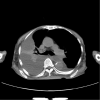
A 91-year-old woman was brought to our hospital with altered consciousness. Blood tests showed an increased ammonia level of 468 μg/dL and a normal liver function. Chest computed tomography showed massive right pleural effusion with loculation. We immediately performed chest drainage using two drainage tubes. The pleural effusate pH was 8.5. We diagnosed her with right empyema leading to hyperammonemia and initiated ampicillin/sulbactam therapy. However, she developed progressive renal failure and died on the third day. Empyema caused by urease-producing bacteria can lead to hyperammonemia. This is the first report of hyperammonemia due to empyema in the English literature.
Keywords: altered consciousness; empyema; hyperammonemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Auron A, Brophy PD. Hyperammonemia in review: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Pediatr Nephorol 27: 207-220, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Inoue H, Nakata T, Namiki M, Yaguchi A. A case of hyperammonemia due to urinary tract infection complicated by hypothyroidism. Nihon Kyukyu Igakkai Zasshi (J Jpn Assoc Acute Med) 23: 398-402, 2012.
-
- Light RW, MacGregor MI, Ball WC, Luchsinger PC. Diagnostic significance of pleural fluid pH and PCO2. Chest 64: 591-596, 1973. - PubMed
-
- Potts DE, Levin DC, Sahn SA. Pleural fluid pH in parapneumonic effusions. Am J Med 70: 328-331, 1980. - PubMed
-
- Shen KR, Bribriesco A, Crabtree T, et al. The American Association for Thoracic Surgery consensus guidelines for the management of empyema. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 153: e129-e146, 2017. - PubMed