Single-Cell Landscape Highlights Heterogenous Microenvironment, Novel Immune Reaction Patterns, Potential Biomarkers and Unique Therapeutic Strategies of Cervical Squamous Carcinoma, Human Papillomavirus-Associated (HPVA) and Non-HPVA Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36725337
- PMCID: PMC10074047
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202204951
Single-Cell Landscape Highlights Heterogenous Microenvironment, Novel Immune Reaction Patterns, Potential Biomarkers and Unique Therapeutic Strategies of Cervical Squamous Carcinoma, Human Papillomavirus-Associated (HPVA) and Non-HPVA Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
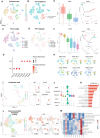
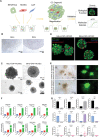
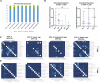
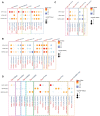
Cervical adenocarcinomas (ADCs), including human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated (HPVA) and non-HPVA (NHPVA), though exhibiting a more malignant phenotype and poorer prognosis, are treated identically to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). This clinical dilemma requires a deeper investigation into their differences. Herein a transcriptomic atlas of SCC, HPVA, and NHPVA-ADC using single-cell RNA (scRNA) and T-cell receptor sequencing (TCR-seq) is presented. Regarding structural cells, the malignancy origin of epithelial cells, angiogenic tip cells and two subtypes of fibroblasts is revealed. The promalignant properties of the structural cells using organoids are further confirmed. Regarding immune cells, myeloid cells with multiple functions other than antigen presentation and exhausted T lymphocytes contribute to immunosuppression. From the perspective of HPV infection, not only is HPV-dependent and independent cervical cancer oncogenesis proposed but also three immune reaction patterns mediated by T cells (coordinated/inactive/imbalanced) are identified. Strikingly, diagnostic biomarkers to distinguish ADC from SCC are discovered and prognostic biomarkers with marker genes for malignant epithelial cells, tip cells, and SPP1/C1QC macrophages are generated. Importantly, the efficacy of anti-CD96 and anti-TIGIT, not inferior to anti-PD1, in animal experiments is confirmed and targeted therapies specifically for HPV-positive SCC, HPVA and NHPVA-ADC, providing essential clues for further clinical trials, are proposed.
Keywords: HPV infection; TCR-seq; cervical cancer; precise treatment; scRNA-seq; transcriptional heterogeneity; tumor microenvironment.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Reimers L. L., Anderson W. F., Rosenberg P. S., Henson D. E., Castle P. E., Cancer Epidemiol., Biomarkers Prev. 2009, 18, 792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81971361/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173188/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22Y3190050/Medical Innovation Research of Shanghai Science and Technology
- 21Y11906900/Medical Innovation Research of Shanghai Science and Technology
- SHDC2020CR1045B/Shanghai Hospital Development Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
