Chronic hepatitis B with concurrent metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Challenges and perspectives
- PMID: 36726053
- PMCID: PMC10121303
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0422
Chronic hepatitis B with concurrent metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Challenges and perspectives
Abstract
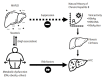
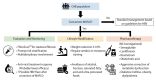
The prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) has increased among the general population and chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients worldwide. Although fatty liver disease is a well-known risk factor for adverse liver outcomes like cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, its interactions with the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and clinical impacts seem complex. The presence of hepatic steatosis may suppress HBV viral activity, potentially leading to attenuated liver injury. In contrast, the associated co-morbidities like diabetes mellitus or obesity may increase the risk of developing adverse liver outcomes. These findings implicate that components of MAFLD may have diverse effects on the clinical manifestations of CHB. To this end, a clinical strategy is proposed for managing patients with concurrent CHB and MAFLD. This review article discusses the updated evidence regarding disease prevalence, interactions between steatosis and HBV, clinical impacts, and management strategies, aiming at optimizing holistic health care in the CHB population.
Keywords: Fatty liver; Hepatitis B virus; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Metabolic syndrome; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Zou B, Yeo YH, Feng Y, Xie X, Lee DH, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:389–398. - PubMed
-
- Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. 2020;73:202–209. - PubMed
-
- Lin S, Huang J, Wang M, Kumar R, Liu Y, Liu S, et al. Comparison of MAFLD and NAFLD diagnostic criteria in real world. Liver Int. 2020;40:2082–2089. - PubMed
-
- Yamamura S, Eslam M, Kawaguchi T, Tsutsumi T, Nakano D, Yoshinaga S, et al. MAFLD identifies patients with significant hepatic fibrosis better than NAFLD. Liver Int. 2020;40:3018–3030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

