Development and Evaluation of Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery System-Based Tablets for Simvastatin, a BCS Class II Drug
- PMID: 36726738
- PMCID: PMC9885879
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S377686
Development and Evaluation of Self-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery System-Based Tablets for Simvastatin, a BCS Class II Drug
Abstract
Background: Self-emulsifying drug-delivery systems (SEDDSs) are designed to improve the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. This study aimed at formulating and characterization of SEDDS-based tablets for simvastatin using castor and olive oils as solvents and Tween 60 as surfactant.
Methods: The liquids were adsorbed on microcrystalline cellulose, and all developed formulations were compressed using 10.5 mm shallow concave round punches.
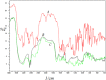
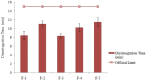
Results: The resulting tablets were evaluated for different quality-control parameters at pre- and postcompression levels. Simvastatin showed better solubility in a mixture of oils and Tween 60 (10:1). All the developed formulations showed lower self-emulsification time (˂200 seconds) and higher cloud point (˃60°C). They were free of physical defects and had drug content within the acceptable range (98.5%-101%). The crushing strength of all formulations was in the range of 58-96 N, and the results of the friability test were within the range of USP (≤1). Disintegration time was within the official limits (NMT 15 min), and complete drug release was achieved within 30 min.
Conclusion: Using commonly available excipients and machinery, SEDDS-based tablets with better dissolution profile and bioavailability can be prepared by direct compression. These S-SEDDSs could be a better alternative to conventional tablets of simvastatin.
Keywords: Tween 60; castor oil; olive oil; self-emulsified drug-delivery system; simvastatin.
© 2023 Bashir et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Amjad K, Zafar I, Yasar S, Lateef A, Ismail Z, Aman U. Enhancement of dissolution rate of class II drugs (Hydrochlorothiazide); a comparative study of the two novel approaches; solid dispersion and liqui-solid techniques. Saudi Pharm J. 2015;23:650–657. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2015.01.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amjad K, Zafar I, Abad K, et al. Formulation and evaluation of taste masked orally disintegrating tablets of itopride HCl using hydrophilic polymers as drug carrier. Latin Am J Pharm. 2015;34(7):1364–1372.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

