Safety and efficacy of low-energy small incision lenticule extraction for the correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism: A retrospective analysis
- PMID: 36727343
- PMCID: PMC10228926
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1757_22
Safety and efficacy of low-energy small incision lenticule extraction for the correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism: A retrospective analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the safety and efficacy of low-energy settings in small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) for correcting myopia and myopic astigmatism.
Methods: We included patients aged ≥18 years with the myopia of -0.5 to -10 D and myopic astigmatism of -0.5 to -5 Dcyl in this retrospective case series performed at a private eye hospital in South India. All patients had preoperative best-corrected visual acuity of LogMar 0.0 ± 0, with stable refraction for 1 year and normal corneal topography. Ocular surface disease and other pathology cases were excluded. The repetition rate of the laser was 500 kHz, and the pulse energy was 110 nJ. The lenticule diameter was set at 6.5 mm, cap diameter was 7.20 mm, and intended cap thickness was 110-130 μ. The spot distance was 4.5 μm. All patients were evaluated immediately postoperation and on postoperative days 1, 8, and 30.
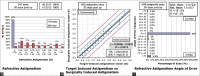
Results: Overall, 541 eyes were included. The mean patient age was 25.03 ± 4.1 years. The mean spherical error was -3.76 ± 1.84 Ds. The mean cylinder was -1.24 ± 0.91. The mean spherical equivalent of refraction was -4.22 ±1.94 D. The logMAR on postoperative day 1 was 0.0 ± 0. The mean spherical equivalent at 1 month was 0.28 ± 1.06 D. There was no loss of Snellen's lines after the procedure. The mean spherical equivalent of refraction to the target was 95% within ± 0.50 D. The postoperative astigmatism was within 0.5 Dycl. No intraoperative complications of SMILE including retained lenticule fragments, tears of incision, or improper dissection occurred.
Conclusion: Low-energy settings in SMILE are safe and effective in correcting myopia and myopic astigmatism including high cylinders (>3 Dcyl).
Keywords: Femtosecond; LASIK; SMILE.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- Sugar A, Rapuano CJ, Culbertson WW, Huang D, Varley GA, Agapitos PJ, et al. Laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia and astigmatism:Safety and efficacy. A report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:175–87. - PubMed
-
- Schallhorn SC, Farjo AA, Huang D, Wachler BS, Trattler WB, Tanzer DJ, et al. Wavefront-guided LASIK for the correction of primary myopia and astigmatism. A report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:1249–61. - PubMed
-
- Stonecipher K, Ignacio TS, Stonecipher M. Advances in refractive surgery:Microkeratome and femtosecond laser flap creation in relation to safety, efficacy, predictability, and biomechanical stability. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006;17:368–72. - PubMed
-
- Reinstein DZ, Carp GI, Archer TJ, Lewis TA, Gobbe M, Moore J, et al. Long-term visual and refractive outcomes after LASIK for high myopia and astigmatism from -8.00 to -14.25 D. J Refract Surg. 2016;32:290–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

