Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Elderly Patients with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- PMID: 36727811
- PMCID: PMC9924965
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003813
Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Elderly Patients with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abstract
Background: The cause of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) is uncertain in a significant number of patients. A vascular etiology has been proposed because SSNHL increases the risk of developing a stroke. Cardiovascular risk factors can cause cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD). The presence of CSVD in turn raises the risk of stroke.
Aim: The aim of this study was to compare the presence of CSVD and cardiovascular risk factors in elderly patients with idiopathic SSNHL (iSSNHL) to a control cohort.
Method: Patients with iSSNHL of 50 years and older were compared with a control cohort with patients suspected of trigeminal neuralgia or vestibular paroxysmia. The primary outcome was the difference in the number of white matter hyperintensities using the ordinal Fazekas scale. Secondary outcomes were the presence of brain infarctions on MRI and the difference in cardiovascular risk factors.
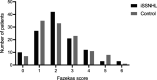
Results: In the SSNHL cohort, Fazekas score 2 was most frequently seen compared with Fazekas 1 in the control cohort. The distribution of Fazekas scores did not differ significantly. The sum of the Fazekas scores were 13,925 and 14,042 for iSSNHL and controls, respectively ( p = 0.908). Brain infarctions were seen in 8 patients with iSSNHL (n = 118) and in 13 patients in the control cohort (n = 118) ( p = 0.361). None of the cardiovascular risk factors were more frequently seen in the iSSNHL cohort.
Conclusion: Patients with iSSNHL did not exhibit more CSVD on MRI than controls. This result is in contrast with previous literature demonstrating a higher risk of stroke in patients with iSSNHL than in controls. A prospective analysis with a larger study population is therefore warranted.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of Otology & Neurotology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2010;120:1011–21. - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekhar SS Tsai Do BS Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2019;161(suppl 1):S1–S45. - PubMed
-
- Alexander TH, Harris JP. Incidence of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 2013;34:1586–9. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Ding L. Effectiveness of steroid treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Pharmacother 2020;54:949–57. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

