Evaluation of the Revised Versus Original Ryan White Part A HIV Care Coordination Program in a Cluster-Randomized, Stepped-Wedge Trial
- PMID: 36729538
- PMCID: PMC9936966
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003139
Evaluation of the Revised Versus Original Ryan White Part A HIV Care Coordination Program in a Cluster-Randomized, Stepped-Wedge Trial
Abstract
Background: To address challenges with delivery of an evidence-based HIV care coordination program (CCP), the New York City Health Department initiated a CCP redesign. We conducted a site-randomized stepped-wedge trial to evaluate effectiveness of the revised versus the original model.
Setting: The CCP is delivered in New York City hospitals, community health centers, and community-based organizations to people experiencing or at risk for poor HIV outcomes.
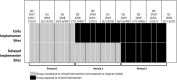
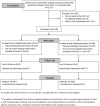
Methods: The outcome, timely viral suppression (TVS), was defined as achievement of viral load <200 copies/mL within 4 months among enrollees with unsuppressed viral load (≥200 copies/mL). Seventeen original-CCP provider agencies were randomized within matched pairs to early (August 2018) or delayed (May 2019) starts of revised-model implementation. Data from 3 periods were examined to compare revised versus original CCP effects on TVS. The primary analysis of the intervention effect applied fully conditional maximum likelihood estimation together with an exact, conditional P -value and an exact test-based 95% CI. We assigned each trial enrollee the implementation level of their site (based on a three-component measure) and tested for association with TVS, adjusting for period and study arm.
Results: Over 3 nine-month periods, 960 individuals were eligible for trial inclusion (intention to treat). The odds ratio of TVS versus no TVS comparing revised with original CCP was 0.88 (95% CI: 0.45, 1.7). Thus, the revised program yielded slightly lower TVS, although the effect was statistically nonsignificant. TVS was not significantly associated with revised-CCP implementation level.
Conclusion: Program revisions did not increase TVS, irrespective of the implementation level.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03628287.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- The TEMPRANO ANRS 12136 Study Group. A trial of early antiretrovirals and isoniazid preventive therapy in Africa. New Engl J Med. 2015;373:808–822. - PubMed