Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Lactulose and Rifaximin on Patient-Reported Outcomes in Hepatic Encephalopathy
- PMID: 36730910
- PMCID: PMC9904367
- DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002008
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Lactulose and Rifaximin on Patient-Reported Outcomes in Hepatic Encephalopathy
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with hepatic encephalopathy (HE) suffer from significant symptoms and impaired quality of life. Improved understanding on the potential benefits of first-line HE therapies may aid patient-provider discussions regarding expected benefits of HE treatments. We aimed to perform a systematic review to assess the effects of lactulose and rifaximin on patient-reported outcomes (PROs).
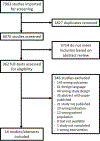
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library databases for randomized trials or prospective cohort studies using lactulose and/or rifaximin for the management of HE and assessing changes in PRO using PRO instruments. Physician reviewers independently reviewed titles, abstracts, and full texts and extracted data independently. We performed random-effects meta-analyses to examine the effects of lactulose and rifaximin on PROs.
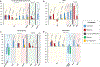
Results: We identified 16 studies representing 1,376 patients that met inclusion criteria. Most studies assessed treatment of covert HE. In patients with covert HE, lactulose significantly improved overall patient-reported health-related quality of life measured by the Sickness Impact Profile with an estimated pooled mean difference of 6.92 (95% confidence interval: 6.66-7.18) and showed improvements in several subscales. Conversely, rifaximin demonstrated a nonstatistically significant mean difference in the total Sickness Impact Profile of 4.76 (95% confidence interval: -4.23 to 13.76), with strong evidence of heterogeneity between these studies. Studies examining other PRO instruments showed improvements in overall health-related quality of life, social functioning, and sleep from both lactulose and rifaximin.
Discussion: Patients with HE treated with lactulose or rifaximin reported improvements in important PROs. These results may inform provider-patient communication and help manage patient expectations regarding the potential benefits of HE therapies.
Copyright © 2022 by The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
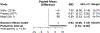
References
-
- Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy--definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 2002;35:716–21. - PubMed
-
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014;60:715–35. - PubMed
-
- American Association for the Study of Liver D, European Association for the Study of the L. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. J Hepatol 2014;61:642–59. - PubMed
-
- Kimer N, Krag A, Moller S, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effects of rifaximin in hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014;40:123–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

