Flecainide toxicity: ECG changes associated with supratherapeutic levels in milk-fed infants
- PMID: 36731946
- PMCID: PMC9896187
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-252823
Flecainide toxicity: ECG changes associated with supratherapeutic levels in milk-fed infants
Abstract
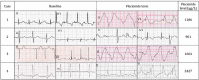
Flecainide is a class 1C antiarrhythmic and is highly effective for treating a wide range of arrhythmias. It is not licensed for children under the age of 12 years, but has been used safely for years in young children, particularly when first-line agents are not effective. Although toxicity does occur in both adult and paediatric populations, there have been very few reported instances of flecainide toxicity in neonates and children. Supratherapeutic levels of flecainide manifests on ECG with prolongation of the PR interval, QRS duration and QT, and can lead to life-threatening arrhythmias. In milk-fed infants receiving flecainide, regular feeding patterns are paramount to achieve a steady therapeutic state, as milk and dairy products are known to reduce the absorption of flecainide. This case series details four milk-fed infants admitted with ECG changes secondary to flecainide toxicity.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; Cardiovascular system; Neonatal and paediatric intensive care; Paediatrics (drugs and medicines); Unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials