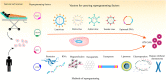
Induced pluripotent stem cells: Generation methods and a new perspective in COVID-19 research
- PMID: 36733338
- PMCID: PMC9887183
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1050856
Induced pluripotent stem cells: Generation methods and a new perspective in COVID-19 research
Abstract
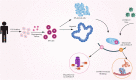
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) exhibit an unlimited ability to self-renew and produce various differentiated cell types, thereby creating high hopes for both scientists and patients as a great tool for basic research as well as for regenerative medicine purposes. The availability and safety of iPSCs for therapeutic purposes require safe and highly efficient methods for production of these cells. Different methods have been used to produce iPSCs, each of which has advantages and disadvantages. Studying these methods would be very helpful in developing an easy, safe, and efficient method for the generation of iPSCs. Since iPSCs can be generated from somatic cells, they can be considered as valuable cellular resources available for important research needs and various therapeutic purposes. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a disease that has endangered numerous human lives worldwide and currently has no definitive cure. Therefore, researchers have been rigorously studying and examining all aspects of COVID-19 and potential treatment modalities and various drugs in order to enable the treatment, control, and prevention of COVID-19. iPSCs have become one of the most attractive and promising tools in this field by providing the ability to study COVID-19 and the effectiveness of drugs on this disease outside the human body. In this study, we discuss the different methods of generation of iPSCs as well as their respective advantages and disadvantages. We also present recent applications of iPSCs in the study and treatment of COVID-19.
Keywords: disease modeling; drug screening; mRNA; pluripotency; reprogramming; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2023 Karami, Moradi, Eidi, Soleimani and Jafarian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abo K. M., Human iPSC-derived alveolar and airway epithelial cells can be cultured at air-liquid interface and express SARS-CoV-2 host factors. Biorxiv, 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources