Application of microfluidic chip electrophoresis for high-throughput nucleic acid fluorescence fragment analysis assays
- PMID: 36733401
- PMCID: PMC9887644
- DOI: 10.1093/nargab/lqad011
Application of microfluidic chip electrophoresis for high-throughput nucleic acid fluorescence fragment analysis assays
Abstract
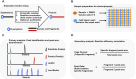
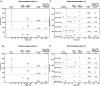
Nucleic acid fragment analysis via separation and detection are routine operations in molecular biology. However, analysis of small single-stranded nucleic acid fragments (<100nt) is challenging and mainly limited to labor-intensive polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or high-cost capillary electrophoresis methods. Here we report an alternative method, a microfluidic chip electrophoresis system that provides a size resolution of 5nt and a detection time of one minute per sample of fluorescence-labeled DNA/RNA fragments. The feasibility of this system was evaluated by quantifying CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage efficiency and the detection resolution was evaluated by analyzing ssDNA/RNA adenylation and phosphorylation. We employed this system to study the RNA capping efficiency and double-stranded DNA unwinding efficiency in isothermal amplification as two examples for assay design and evaluation. The microfluidic chip electrophoresis system provides a rapid, sensitive, and high-throughput fluorescence fragment analysis (FFA), and can be applied for enzyme characterization, reaction optimization, and product quality control in various molecular biology processes.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics.
Figures

References
-
- Wong K.H., Campbell K.L. Factors that affect use of intercalating dyes such as PicoGreen, SYBR Green I, Syto-13 and Syto-82 in DNA assays. Biol. Reprod. 2011; 85:725–725.
-
- Barril P., Nates S. Introduction to agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis matrices with respect to their detection sensitivities. Gel Electrophoresis - Principles and Basics. 2012; InTech.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

