Thrombolytic Dilemma: A Case Report of Early Puerperium Ischemic Stroke Treated With Intravenous Thrombolysis
- PMID: 36733555
- PMCID: PMC9888589
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33204
Thrombolytic Dilemma: A Case Report of Early Puerperium Ischemic Stroke Treated With Intravenous Thrombolysis
Abstract
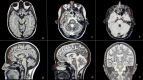
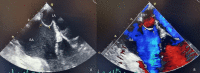
A 25-year-old woman was admitted to the obstetrics ward when presented with a sudden onset of expressive aphasia and minor right facial palsy 48 hours after forceps-assisted delivery. The intrahospital emergency team was immediately mobilized. The patient had a blood pressure (BP) of 119/79 mmHg, heart rate of 114 bpm, O2 saturation of 97%, and blood glucose level of 136 mg/dL. Trauma and toxic exposure were ruled out. A rapid EKG was performed with no significant changes. Assuming an acute stroke, the patient immediately underwent brain CT (approximately 15 minutes after the beginning of the symptoms), which revealed no signs of hemorrhage, an ischemic area, or masses. Brain CT angiography was then performed; however, no major brain artery obstruction was found. With brain hemorrhage ruled out and persistent neurologic deficits, the case was discussed between the emergency team doctor and the patient's obstetrician, and intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) was started approximately 45 minutes after the onset of symptoms. After treatment completion, the patient had a complete resolution of the neurological deficits. The patient remained under strict observation at the acute stroke unit (ASU), and no secondary brain hemorrhage or post-partum-related complications were noted.
Keywords: early puerperium thrombolysis; ischemic stroke; postpartum complication; thrombolytic therapy; tissue plasminogen activator.
Copyright © 2023, Santos et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decrease in blood pressure after intravenous administration of urapidil during recombinant tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke.Clin Ther. 2008 Sep;30(9):1675-80. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.09.005. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18840373
-
Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke.Stroke. 2003 Aug;34(8):e109-37. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000082721.62796.09. Epub 2003 Jul 17. Stroke. 2003. PMID: 12869717
-
Successful intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke caused by aortic dissection with severe hypofibrinogenemia: a case report and literature review.Int J Neurosci. 2022 Sep;132(9):939-944. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1858823. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Int J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 33393403 Review.
-
Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS).JAMA. 1995 Oct 4;274(13):1017-25. JAMA. 1995. PMID: 7563451 Clinical Trial.
-
Uneventful Pregnancy and Delivery after Thrombolysis Plus Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Case Study and Literature Review.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Jan;28(1):70-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 30268366 Review.
References
-
- Acute stroke diagnosis. Yew KS, Cheng E. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2722757/ Am Fam Physician. 2009;80:33–40. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis and management of women with stroke during pregnancy/postpartum. Sibai BM, Coppage KH. Clin Perinatol. 2004;31:853-68, viii. - PubMed
-
- Stroke in pregnancy and the puerperium. Treadwell SD, Thanvi B, Robinson TG. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:238–245. - PubMed
-
- Stroke in the puerperium treated with intra-arterial rt-PA. Rønning OM, Dahl A, Bakke SJ, Hussain AI, Deilkås E. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010;81:585–586. - PubMed
-
- Thrombolytic therapy of acute ischemic stroke during pregnancy. Murugappan A, Coplin WM, Al-Sadat AN, et al. Neurology. 2006;66:768–770. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
