Incidence and long-term specific mortality trends of metabolic syndrome in the United States
- PMID: 36733801
- PMCID: PMC9886893
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1029736
Incidence and long-term specific mortality trends of metabolic syndrome in the United States
Abstract
Purpose: Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is extremely prevalent and related to severe diseases and death. This study aims to investigate the incidence and mortality trends among MetS over the past few decades. The gender and age differences of MetS are also explored.
Patients and methods: Adults with MetS were screened in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 1999 to 2014. The mortality data were also acquired. Then we assessed the incidence and mortality trends of MetS in the United States.
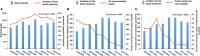
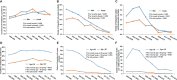
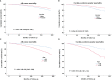
Results: Our study included 14171 participants with a mean age of 46.8 ± 19.3 years, of whom 7354 (51.9%) were women. Among them, 4789 participants were subsequently diagnosed with MetS. From 1999 to 2014, the overall trend of MetS incidence increased (from 27.6 to 32.3%; adjusted odds ratios [aOR], 1.71; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.42-2.05; P-value <0.001, P for trend <0.001). In more detail, the incidence of MetS rose first but subsequently plateaued and declined. Obvious downward trends were observed from 29.6 to 2.7% for all-cause mortality (aOR, 0.12; 95%CI, 0.07-0.21; P-value <0.001, P for trend <0.001) and 4.8 to 0.8% for cardio-cerebrovascular mortality (aOR, 0.17; 95%CI, 0.05-0.61; P-value =0.007, P for trend <0.001). All-cause mortality decreased yearly, whereas cardio-cerebrovascular death increased briefly before declining and stabilizing. Similarly, the temporal mortality trends in MetS patients of different ages and genders had the same results. Specifically, the incidence of MetS was higher in women than in men (adjusted P =0.003; OR, 1.14; 95%CI, 1.05-1.24), but the mortality was significantly lower after an average of 7.7 years of follow-up (all-cause mortality, adjusted P <0.001; hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95%CI, 0.57-0.81; cardio-cerebrovascular mortality, adjusted P =0.004; HR, 0.55; 95%CI, 0.37-0.83).
Conclusion: From 1999 to 2014, the incidence of MetS in U.S. adults significantly increased overall, while the mortality rate of MetS had a considerable downward trend. Both trends showed marked gender differences, being more prevalent and at lower risk in women compared with men. It is important to identify the factors that will curb the incidence of MetS and decrease mortality, especially in male patients.
Keywords: NHANES; incidence; metabolic syndrome; mortality; trend.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Qiu, Ma and Geng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Noubiap JJ, Nansseu JR, Lontchi-Yimagou E, Nkeck JR, Nyaga UF, Ngouo AT, et al. Geographic distribution of metabolic syndrome and its components in the general adult population: A meta-analysis of global data from 28 million individuals. Diabetes Res Clin Pract (2022) 188:109924. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109924 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

