Modeling Syphilis and HIV Coinfection: A Case Study in the USA
- PMID: 36735105
- PMCID: PMC9897625
- DOI: 10.1007/s11538-023-01123-w
Modeling Syphilis and HIV Coinfection: A Case Study in the USA
Abstract
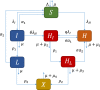
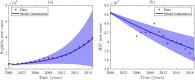
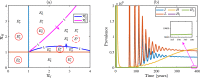
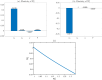
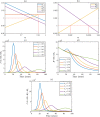
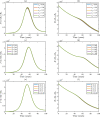
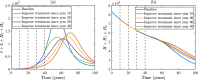
Syphilis and HIV infections form a dangerous combination. In this paper, we propose an epidemic model of HIV-syphilis coinfection. The model always has a unique disease-free equilibrium, which is stable when both reproduction numbers of syphilis and HIV are less than 1. If the reproduction number of syphilis (HIV) is greater than 1, there exists a unique boundary equilibrium of syphilis (HIV), which is locally stable if the invasion number of HIV (syphilis) is less than 1. Coexistence equilibrium exists and is stable when all reproduction numbers and invasion numbers are greater than 1. Using data of syphilis cases and HIV cases from the US, we estimated that both reproduction numbers for syphilis and HIV are slightly greater than 1, and the boundary equilibrium of syphilis is stable. In addition, we observed competition between the two diseases. Treatment for primary syphilis is more important in mitigating the transmission of syphilis. However, it might lead to increase of HIV cases. The results derived here could be adapted to other multi-disease scenarios in other regions.
Keywords: Coinfection; Epidemic model; HIV transmission; Invasion numbers; Reproduction numbers; Syphilis infection.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Society for Mathematical Biology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coinfection dynamics of heroin transmission and HIV infection in a single population.J Biol Dyn. 2020 Dec;14(1):116-142. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2020.1726516. J Biol Dyn. 2020. PMID: 32065067
-
Mathematical Analysis of the Transmission Dynamics of HIV Syphilis Co-infection in the Presence of Treatment for Syphilis.Bull Math Biol. 2018 Mar;80(3):437-492. doi: 10.1007/s11538-017-0384-0. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Bull Math Biol. 2018. PMID: 29282597
-
Modeling and Research on an Immuno-Epidemiological Coupled System with Coinfection.Bull Math Biol. 2021 Oct 13;83(11):116. doi: 10.1007/s11538-021-00946-9. Bull Math Biol. 2021. PMID: 34643801 Free PMC article.
-
Global challenges in human immunodeficiency virus and syphilis coinfection among men who have sex with men.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016 Nov;14(11):1037-1046. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2016.1236683. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016. PMID: 27626361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syphilis and HIV: a dangerous combination.Lancet Infect Dis. 2004 Jul;4(7):456-66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(04)01061-8. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15219556 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding HIV/AIDS dynamics: insights from CD4+T cells, antiretroviral treatment, and country-specific analysis.Front Public Health. 2024 Apr 11;12:1324858. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1324858. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38665242 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Syphilis Infection and HIV Acquisition and HIV Disease Progression in Sub-Saharan Africa.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 28;10(3):65. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed10030065. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40137819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai L, Li X, Ghosh M, Guo B. Stability analysis of an HIV/AIDS epidemic model with treatment. J Comput Appl Math. 2009;229(1):313–323. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2008.10.067. - DOI
-
- CDC (2022a) Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/default.htm
-
- CDC (2022b) HIV surveillance reports. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/hiv-surveillance.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

