The Oral PI3Kδ Inhibitor Linperlisib for the Treatment of Relapsed and/or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: A Phase II, Single-Arm, Open-Label Clinical Trial
- PMID: 36735519
- PMCID: PMC10102838
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2939
The Oral PI3Kδ Inhibitor Linperlisib for the Treatment of Relapsed and/or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: A Phase II, Single-Arm, Open-Label Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the efficacy and safety of the novel orally active PI3Kδ inhibitor in relapsed and/or refractory patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) who had received at least two prior systemic treatments.
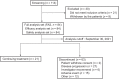
Patients and methods: Histologically confirmed relapsed and/or refractory patients with FL with disease progression after receiving second-line or greater systemic therapy were enrolled. Linperlisib was administered at 80 mg every day, orally in a 28-day cycle until disease progression or intolerable toxicity occurred. The primary outcome for the study was the objective response rate (ORR), with secondary outcomes including the duration of response (DOR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), disease control rate, and drug safety profile.
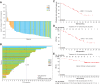
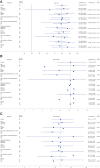
Results: Of 114 screened relapsed and/or refractory patients with FL, 84 were enrolled in the full analysis set (FAS). The ORR of the 84 FAS patients was 79.8% [95% confidence interval (CI), 69.6-87.8, 67 patients], with 13 patients (15.5%) achieving a complete response and 54 patients (64.3%) with a partial response. The median DOR was 12.3 months (95% CI, 9.3-15.9). The median PFS was 13.4 months (95% CI, 11.1-16.7). The 12-month OS rate was 91.4% (95% CI, 82.7-95.8) and a median OS not reached by 42 months. The most frequent (>3%) treatment-related adverse events Grade ≥3 were infectious pneumonia (19.0%), neutropenia (15.5%), decreased lymphocyte count (4.8%), decreased leukocyte count (4.8%), increased lipase (3.6%), decreased platelet count (3.6%), hypertriglyceridemia (3.6%), and interstitial lung disease (3.6%).
Conclusions: Linperlisib demonstrated compelling clinical activity and manageable tolerability for relapsed and/or refractory patients with FL who had received at least two prior systemic therapies.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Comment in
- 1078-0432. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-29-8-HI
Similar articles
-
Polatuzumab vedotin plus obinutuzumab and lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: a cohort of a multicentre, single-arm, phase 1b/2 study.Lancet Haematol. 2021 Dec;8(12):e891-e901. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00311-2. Lancet Haematol. 2021. PMID: 34826412 Clinical Trial.
-
Obinutuzumab combined with lenalidomide for relapsed or refractory follicular B-cell lymphoma (GALEN): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Haematol. 2019 Aug;6(8):e429-e437. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30089-4. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Lancet Haematol. 2019. PMID: 31296423 Clinical Trial.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Safety and efficacy of mosunetuzumab, a bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2022 Aug;23(8):1055-1065. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00335-7. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Lancet Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35803286 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical outcomes in patients relapsed/refractory after ≥2 prior lines of therapy for follicular lymphoma: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jan 23;23(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10546-6. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36690960 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Silico Discovery of a Novel PI3Kδ Inhibitor Incorporating 3,5,7-Trihydroxychroman-4-one Targeting Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 19;25(20):11250. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011250. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457034 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorinated small molecule derivatives in cancer immunotherapy: emerging frontiers and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 18;16:1622091. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1622091. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40755757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse role, structural trends, and applications of fluorinated sulphonamide compounds in agrochemical and pharmaceutical fields.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 8;10(12):e32434. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32434. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38975170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule agents for cancer immunotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Mar;14(3):905-952. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.12.010. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38486980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JMC14: a novel dual PI3Kδ/CSF1R inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in hematological and solid tumors.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May 19. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01575-x. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40389566
References
-
- Fischer T, Zing NPC, Chiattone CS, Federico M, Luminari S. Transformed follicular lymphoma. Ann Hematol 2018;97:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Luminari S, Ferrari A, Manni M, Dondi A, Chiarenza A, Merli F, et al. . Long-term results of the FOLL05 trial comparing R-CVP versus R-CHOP versus R-FM for the initial treatment of patients with advanced-stage symptomatic follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2018;36:689–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

