Arginine metabolism regulates human erythroid differentiation through hypusination of eIF5A
- PMID: 36735910
- PMCID: PMC10273172
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022017584
Arginine metabolism regulates human erythroid differentiation through hypusination of eIF5A
Abstract
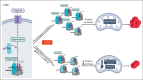
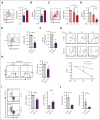
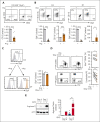
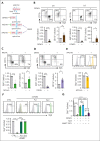
Metabolic programs contribute to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) fate, but it is not known whether the metabolic regulation of protein synthesis controls HSPC differentiation. Here, we show that SLC7A1/cationic amino acid transporter 1-dependent arginine uptake and its catabolism to the polyamine spermidine control human erythroid specification of HSPCs via the activation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A). eIF5A activity is dependent on its hypusination, a posttranslational modification resulting from the conjugation of the aminobutyl moiety of spermidine to lysine. Notably, attenuation of hypusine synthesis in erythroid progenitors, by the inhibition of deoxyhypusine synthase, abrogates erythropoiesis but not myeloid cell differentiation. Proteomic profiling reveals mitochondrial translation to be a critical target of hypusinated eIF5A, and accordingly, progenitors with decreased hypusine activity exhibit diminished oxidative phosphorylation. This affected pathway is critical for eIF5A-regulated erythropoiesis, as interventions augmenting mitochondrial function partially rescue human erythropoiesis under conditions of attenuated hypusination. Levels of mitochondrial ribosomal proteins (RPs) were especially sensitive to the loss of hypusine, and we find that the ineffective erythropoiesis linked to haploinsufficiency of RPS14 in chromosome 5q deletions in myelodysplastic syndrome is associated with a diminished pool of hypusinated eIF5A. Moreover, patients with RPL11-haploinsufficient Diamond-Blackfan anemia as well as CD34+ progenitors with downregulated RPL11 exhibit a markedly decreased hypusination in erythroid progenitors, concomitant with a loss of mitochondrial metabolism. Thus, eIF5A-dependent protein synthesis regulates human erythropoiesis, and our data reveal a novel role for RPs in controlling eIF5A hypusination in HSPCs, synchronizing mitochondrial metabolism with erythroid differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.S., S.K., and N.T. are inventors on patents describing the use of RBD ligands but N.T. no longer has any patent rights. M.S. is the cofounder of METAFORA-biosystems, a start-up company that focuses on metabolite transporters under physiological and pathological conditions. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

