Sufficient versus deficient rims during percutaneous closure of ostium secundum type atrial septal defect: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36736460
- PMCID: PMC10123416
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2023.01.008
Sufficient versus deficient rims during percutaneous closure of ostium secundum type atrial septal defect: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The aim of this meta-analysis was to compare the efficacy and adverse events of percutaneous occlusion among patients with sufficient and deficient rims.
Methods: A systematic review of all articles published in the Pubmed, MEDLINE and Google Scholar databases was performed. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI were used as a measure of effect of the combination of studies. I2 with 95% CI was estimated to assess study heterogeneity. For the meta-analysis, a random effects model was used.
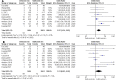
Results: The systematic search identified ten studies which included 4355 patients; 2661 of those had sufficient rim and the remaining 1694 patients showed some rim deficiency. Implant failure rate was 4.13% CI 95% 3.53-4.72%. Compared to frequency of failures in the group with a deficient rim (5.43% CI 95% 4.35-6.50%), implant failure in patients with a sufficient rim was significantly lower (3.30% CI 95% 2.62-3.97%), OR 2.27 CI 1.34-3.83 (p 0.002). The combined adverse events were 5.19% CI 95% 4.22-6.35% vs 2.7% CI 95% 2.08-3.31% in the deficient vs sufficient rim groups respectively (OR 2.21 CI 0.93-5.29; p 0.07). Implant failures and adverse events were more frequent in patients with posterior inferior rim deficiency.
Conclusion: Patients presenting a posteroinferior rim deficiency are associated to both, an increased incidence of closure failure and a combined adverse events occurrence. More studies on posterior rim deficiency are necessary to ensure the feasibility and safety of the percutaneous approach.
Keywords: Adverse events; Atrial septal defect; Echocardiography; Efficacy.
Copyright © 2023 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier, a division of RELX India, Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest No author has conflicts of interest. The authors have not received financial support for the development of the research.
Figures


References
-
- Stout K.K., Daniels C.J., Aboulhosn J.A., et al. AHA/ACC guideline for the management of adults with congenital heart disease: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;73(12):e81–e192. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.1029. 2019 Apr 2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amin Z., Hijazi Z.M., Bass J.L., Cheatham J.P., Hellenbrand W.E., Kleinman C.S. Erosion of Amplatzer septal occluder device after closure of secundum atrial septal defects: review of registry of complications and recommendations to minimize future risk. Cathet Cardiovasc Interv. 2004 Dec;63(4):496–502. doi: 10.1002/ccd.20211. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

