Comparison of the efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy and sorafenib alone or combined for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis
- PMID: 36737488
- PMCID: PMC10543878
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-023-00997-3
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy and sorafenib alone or combined for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) is a developing technique and its efficacy and modality of application in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are still controversial. This network meta-analysis aims to determine whether the efficacy and safety of SIRT alone and in combination are superior to that of sorafenib.
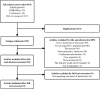
Methods: Four databases (PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science) were searched before August 2022. Cochrane Randomized Trial Risk of Bias Assessment Tool and the Newcastle-Ottawa scale were used to assess the quality. The outcomes of interest included overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and adverse events (AEs).
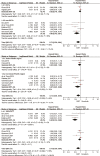
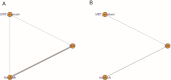
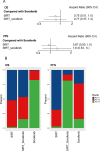
Results: A total of 9 eligible trials involving 1954 patients were included, and SIRT ranked first among the three treatment modalities in terms of both OS (probability, 52.3%) and PFS (probability, 68.6%). The combination of SIRT and sorafenib did not improve OS or PFS in patients with HCC. Although the combination of SIRT and sorafenib did not raise the risk of grade 3 or higher AEs, it may have introduced more AEs than either alone.
Conclusions: SIRT alone was found to be superior to sorafenib and the combination of the two in improving OS or PFS in patients with non-surgical HCC, especially in patients with combined portal vein tumor thrombus. The AEs induced by SIRT were different from those of sorafenib, but the overall toxicity was manageable, the combination of the two may cause an increase in the types of AEs that occur.
Keywords: Liver cancer; Network meta-analysis; Non-surgical treatments; Transarterial radioembolization; Yttrium-90.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sequencing of systemic therapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Dec;204:104522. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104522. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39332750
-
External beam radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 7;3(3):CD011314. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011314.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28267205 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
-
Ablative and non-surgical therapies for early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2023 Dec;27(29):1-172. doi: 10.3310/GK5221. Health Technol Assess. 2023. PMID: 38149643 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib for the management of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 4;18(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12876-018-0849-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30180810 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in Radionuclides and Radiolabelled Peptides for Cancer Therapeutics.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 17;15(3):971. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030971. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sorafenib with or without co-interventions for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 26;6(6):CD015851. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015851. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40568833 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

