Spinophilin-dependent regulation of GluN2B-containing NMDAR-dependent calcium influx, GluN2B surface expression, and cleaved caspase expression
- PMID: 36738175
- PMCID: PMC11648995
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.22264
Spinophilin-dependent regulation of GluN2B-containing NMDAR-dependent calcium influx, GluN2B surface expression, and cleaved caspase expression
Abstract
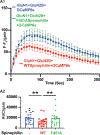
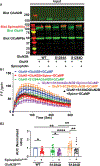
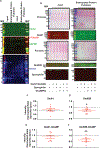
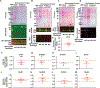
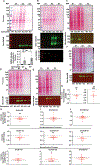
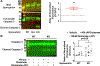
N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are calcium-permeable ion channels that are ubiquitously expressed within the glutamatergic postsynaptic density. Phosphorylation of NMDAR subunits defines receptor conductance and surface localization, two alterations that can modulate overall channel activity. Modulation of NMDAR phosphorylation by kinases and phosphatases regulates the amount of calcium entering the cell and subsequent activation of calcium-dependent processes. The dendritic spine enriched protein, spinophilin, is the major synaptic protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) targeting protein. Depending on the substrate, spinophilin can act as either a PP1 targeting protein, to permit substrate dephosphorylation, or a PP1 inhibitory protein, to enhance substrate phosphorylation. Spinophilin limits NMDAR function in a PP1-dependent manner. Specifically, we have previously shown that spinophilin sequesters PP1 away from the GluN2B subunit of the NMDAR, which results in increased phosphorylation of Ser-1284 on GluN2B. However, how spinophilin modifies NMDAR function is unclear. Herein, we utilize a Neuro2A cell line to detail that Ser-1284 phosphorylation increases calcium influx via GluN2B-containing NMDARs. Moreover, overexpression of spinophilin decreases GluN2B-containing NMDAR activity by decreasing its surface expression, an effect that is independent of Ser-1284 phosphorylation. In hippocampal neurons isolated from spinophilin knockout animals, there is an increase in cleaved caspase-3 levels, a marker of calcium-associated apoptosis, compared with wildtype mice. Taken together, our data demonstrate that spinophilin regulates GluN2B containing NMDAR phosphorylation, channel function, and trafficking and that loss of spinophilin enhances neuronal cleaved caspase-3 expression.
Keywords: calcium; glutamatergic; hippocampus; phosphatase; signal transduction; synapse.
© 2023 The Authors. Synapse published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spinophilin regulates phosphorylation and interactions of the GluN2B subunit of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor.J Neurochem. 2019 Oct;151(2):185-203. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14831. Epub 2019 Aug 2. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 31325175 Free PMC article.
-
NMDAR-Activated PP1 Dephosphorylates GluN2B to Modulate NMDAR Synaptic Content.Cell Rep. 2019 Jul 9;28(2):332-341.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.030. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31291571 Free PMC article.
-
Spinophilin-Targeted Protein Phosphatase-1 Alleviated Inflammatory Pain by Negative Control of MEK/ERK Signaling in Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn of Rats.J Neurosci. 2015 Oct 14;35(41):13989-4001. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2293-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26468199 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nonsynaptic GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in excitotoxicity: evidence that fluoxetine selectively inhibits these receptors and may have neuroprotective effects.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Apr;93:32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.10.005. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23089362 Review.
-
Regulation of Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity by Protein Phosphatase 1.J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 7;41(14):3040-3050. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2026-20.2021. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33827970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proximity labeling and orthogonal nanobody pulldown (ID-oPD) approaches to map the spinophilin interactome uncover a putative role for spinophilin in protein homeostasis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 23:2025.01.23.634546. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.23.634546. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39896493 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Affaticati P, Mignen O, Jambou F, Potier MC, Klingel-Schmitt I, Degrouard J, . . . Cohen-Kaminsky S (2011). Sustained calcium signalling and caspase-3 activation involve NMDA receptors in thymocytes in contact with dendritic cells. Cell Death Differ, 18(1), 99–108. doi:10.1038/cdd.2010.79 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen PB, Zachariou V, Svenningsson P, Lepore AC, Centonze D, Costa C, . . . Greengard P (2006). Distinct roles for spinophilin and neurabin in dopamine-mediated plasticity. Neuroscience, 140(3), 897–911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
