Absolute dosimetry for FLASH proton pencil beam scanning radiotherapy
- PMID: 36739297
- PMCID: PMC9899251
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-28192-0
Absolute dosimetry for FLASH proton pencil beam scanning radiotherapy
Abstract
A paradigm shift is occurring in clinical oncology exploiting the recent discovery that short pulses of ultra-high dose rate (UHDR) radiation-FLASH radiotherapy-can significantly spare healthy tissues whilst still being at least as effective in curing cancer as radiotherapy at conventional dose rates. These properties promise reduced post-treatment complications, whilst improving patient access to proton beam radiotherapy and reducing costs. However, accurate dosimetry at UHDR is extremely complicated. This work presents measurements performed with a primary-standard proton calorimeter and derivation of the required correction factors needed to determine absolute dose for FLASH proton beam radiotherapy with an uncertainty of 0.9% (1[Formula: see text]), in line with that of conventional treatments. The establishment of a primary standard for FLASH proton radiotherapy improves accuracy and consistency of the dose delivered and is crucial for the safe implementation of clinical trials, and beyond, for this new treatment modality.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.A. is on the Clinical Advisory Board of TAE Life Sciences.
Figures
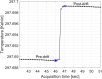
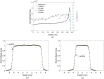
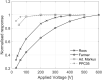


References
-
- Barton MB, et al. Estimating the demand for radiotherapy from the evidence: A review of changes from 2003 to 2012. Radiother. Oncol. 2014;112:140–144. - PubMed
-
- Beadle BM, et al. Improved survival using intensity-modulated radiation therapy in head and neck cancers: A SEER-medicare analysis. Cancer. 2014;120:702–710. - PubMed
-
- Boyer MJ, et al. Improved survival of stage I non-small cell lung cancer: A VA central cancer registry analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017;12:1814–1823. - PubMed
-
- Iacobucci G. Cancer survival in England: Rates improve and variation falls. Br. Med. J. 2019;365:1532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

