Regional Variation of Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent Hyporesponsiveness in the Global Daprodustat Dialysis Study (ASCEND-D)
- PMID: 36739866
- PMCID: PMC10210075
- DOI: 10.1159/000528696
Regional Variation of Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent Hyporesponsiveness in the Global Daprodustat Dialysis Study (ASCEND-D)
Abstract
Introduction: Hyporesponsiveness to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) affects 10-15% of the chronic dialysis population. We explored baseline characteristics and predictors of ESA hyporesponsiveness in a global randomized cardiovascular outcomes study comparing an investigational hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor (HIF-PHI), daprodustat, with conventional ESA treatment.
Methods: ASCEND-D (NCT02879305) recruited 2,964 chronic dialysis patients receiving ESA treatment (standardized to weekly intravenous [IV] epoetin) who were iron replete at baseline. The primary ESA hyporesponsiveness definition was an ESA Resistance Index (ERI, ESA units/kg/week/hemoglobin g/L) ≥2 or IV standardized ESA dose ≥450 units/kg/week. Predictors of ESA hyporesponsiveness were determined using a multivariable regression model. Alternative hyporesponder definitions were explored.
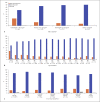
Results: Using the primary definition, 354 (12%) patients were ESA hyporesponsive. Geographic region, notably Latin America, lower baseline body mass index and transferrin saturation, younger age, lower albumin concentration, and a higher baseline IV iron dose were identified as strongly associated (p < 0.001) with ESA hyporesponsiveness. Additional predictors of ESA hyporesponsiveness included female sex (p = 0.010), history of heart failure (p = 0.035), longer dialysis vintage (p = 0.077), smoking status (p = 0.247), aspirin use (p = 0.121), and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker use (p = 0.214).
Conclusion: This is the first global HIF-PHI study to report prespecified definitions and predictors of ESA hyporesponsiveness. While most of the predictors identified in our study have been previously reported, geographic region stands out as an unexpected finding, meriting further investigation.
Keywords: Anemia; Clinical trial; Dialysis; Erythropoiesis-stimulating agent; Hemoglobin.
The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Iain C. Macdougall has received advisory fees from Vifor Pharma, provided advisory services to GSK, and is an ASCEND steering committee member. Sergio Godoy provides consultant services to George Clinical, which involve clinical trials for a range of sponsors. Vivekanand Jha has participated in scientific advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GSK and Boehringer Ingelheim and is an ASCEND steering committee member. Kirsten L. Johansen received ASN fees as JASN Associate Editor, has been an advisory board member for Akebia Therapeutics Inc. and GSK, and is an ASCEND steering committee member. Gearoid McMahon worked as a coordinator for GSK. Gregorio T. Obrador has been a conference speaker and an advisory board member for Roche Mexico, a National Leader for the CREDENCE trial for Janssen Research & Development, LLC, an advisory board member for GSK, and is an ASCEND steering committee member. Muh Geot Wong has received honorarium for scientific lectures from AstraZeneca, Retrophin, Amgen, and Baxter. His employer, the George Institute for Global Health, holds research contracts for trials in cardiovascular and/or kidney disease with a range of commercial organizations. Ajay K. Singh reports consultancy fees from GSK and is an ASCEND steering committee member, Zydus, and BayerAG. Allison Blackorby, Borut Cizman, Alexander R. Cobitz, and Amy M. Meadowcroft are employees of and stockholders in GSK.
Figures
References
-
- Ma JZ, Ebben J, Xia H, Collins AJ. Hematocrit level and associated mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 Mar;10((3)):610–619. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DW, Pascoe EM, Badve SV, Dalziel K, Cass A, Clarke P, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of pentoxifylline on erythropoiesis-stimulating agent hyporesponsiveness in anemic patients with CKD the handling erythropoietin resistance with oxpentifylline (HERO) trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Jan;65((1)):49–57. - PubMed