Predicting Severity of Radiation Induced Lymphopenia in Individual Proton Therapy Patients for Varying Dose Rate and Fractionation Using Dynamic 4-Dimensional Blood Flow Simulations
- PMID: 36739919
- PMCID: PMC10363211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.01.054
Predicting Severity of Radiation Induced Lymphopenia in Individual Proton Therapy Patients for Varying Dose Rate and Fractionation Using Dynamic 4-Dimensional Blood Flow Simulations
Abstract
Purpose: Radiation-induced lymphopenia has gained attention recently as the result of its correlation with survival in a range of indications, particularly when combining radiation therapy (RT) with immunotherapy. The purpose of this study is to use a dynamic blood circulation model combined with observed lymphocyte depletion in patients to derive the in vivo radiosensitivity of circulating lymphocytes and study the effect of RT delivery parameters.
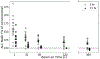
Methods and materials: We assembled a cohort of 17 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with proton RT alone in 15 fractions (fx) using conventional dose rates (beam-on time [BOT], 120 seconds) for whom weekly absolute lymphocyte counts (ALCs) during RT and follow-up were available. We used HEDOS, a time-dependent, whole-body, blood flow computational framework, in combination with explicit liver blood flow modeling, to calculate the dose volume histograms for circulating lymphocytes for changing BOTs (1 second-300 seconds) and fractionations (5 fx, 15 fx). From this, we used the linear cell survival model and an exponential model to determine patient-specific lymphocyte radiation sensitivity, α, and recovery, σ, respectively.
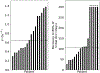
Results: The in vivo-derived patient-specific α had a median of 0.65 Gy-1 (range, 0.30-1.38). Decreasing BOT to 1 second led to an increased average end-of-treatment ALC of 27.5%, increasing to 60.3% when combined with the 5-fx regimen. Decreasing to 5 fx at the conventional dose rate led to an increase of 17.0% on average. The benefit of both increasing dose rate and reducing the number of fractions was patient specificࣧpatients with highly sensitive lymphocytes benefited most from decreasing BOT, whereas patients with slow lymphocyte recovery benefited most from the shorter fractionation regimen.
Conclusions: We observed that increasing dose rate at the same fractionation reduced ALC depletion more significantly than reducing the number of fractions. High-dose-rates led to an increased sparing of lymphocytes when shortening the fractionation regimen, particularly for patients with radiosensitive lymphocytes at elevated risk.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
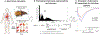

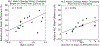
References
-
- Venkatesulu BP, Mallick S, Lin SH, Krishnan S. A systematic review of the influence of radiation-induced lymphopenia on survival outcomes in solid tumors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2018;123:42–51. - PubMed
-
- Damen PJJ, Kroese TE, van Hillegersberg R, et al. The influence of severe radiation-induced lymphopenia on overall survival in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2021;111:936–948. - PubMed
-
- Ellsworth SG, Yalamanchali A, Zhang H, Grossman SA, Hobbs R, Jin JY. Comprehensive analysis of the kinetics of radiation-induced lymphocyte loss in patients treated with external beam radiation therapy. Radiat Res 2019;193:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Carr BI, Metes DM. Peripheral blood lymphocyte depletion after hepatic arterial 90Yttrium microsphere therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012;82:1179–1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

