Developing and validating a nomogram based on skeletal muscle index and clinical scoring system for prediction of liver failure after hepatectomy
- PMID: 36741004
- PMCID: PMC9893412
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1036921
Developing and validating a nomogram based on skeletal muscle index and clinical scoring system for prediction of liver failure after hepatectomy
Abstract
Background and objectives: Hepatectomy is the preferred treatment for patients with liver tumors. Post-hepatectomy liver failure (PHLF) remains one of the most fatal postoperative complications. We aim to explore the risk factors of PHLF and create a nomogram for early prediction of PHLF.
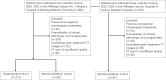
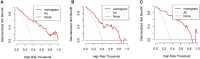
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed patients undergoing hepatectomy at the Affiliated Huaian No. 1 People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University between 2015 and 2022, and the patients were divided into training and internal validation cohorts at an 8:2 ratio randomly. The patients undergoing liver resection from the Affiliated Huaian Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University worked as external validation. Then, a nomogram was developed which was based on multivariate analyses to calculate the risk of PHLF. The area under the ROC curve (AUROC) and Hosmer -Lemeshow test was used to evaluate the prediction effect of the model.
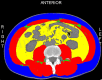
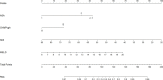
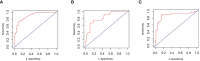
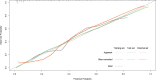
Results: A total of 421 eligible patients were included in our study. Four preoperative variables were identified after multivariate analysis as follows, ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologists) score, Child-Pugh score, SMI (Skeletal muscle index), and MELD (Model for end-stage liver disease) score as independent predictors of PHLF. The area under the ROC curve of the predictive model in the training, internal, and external validation cohorts were 0.89, 0.82, and 0.89. Hosmer -Lemeshow P values in the training, internal, and external validation cohorts were 0.91, 0.22, and 0.15. The Calibration curve confirmed that our nomogram prediction results were in accurate agreement with the actual occurrence of PHLF.
Conclusion: We construct a nomogram to predict the grade B/C PHLF of ISGLS (International Study Group of Liver Surgery) in patients who underwent hepatic resection based on risk factors. This tool can provide a visual and accurate preoperative prediction of the grade B/C PHLF and guide the next step of clinical decision-making.
Keywords: clinical score system; liver; nomogram; post-hepatectomy liver failure; skeletal muscle index.
Copyright © 2023 Ding, Jia, Han, Zhou, Liu, Bai and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Paugam-Burtz C, Janny S, Delefosse D, Dahmani S, Dondero F, Mantz J, et al. Prospective validation of the "fifty-fifty" criteria as an early and accurate predictor of death after liver resection in intensive care unit patients. Ann Surg (2009) 249(1):124–8. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31819279cd - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

