The association of BTLA gene polymorphisms with non-small lung cancer risk in smokers and never-smokers
- PMID: 36741370
- PMCID: PMC9893504
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1006639
The association of BTLA gene polymorphisms with non-small lung cancer risk in smokers and never-smokers
Abstract
Introduction: Lung cancer is the predominant cause of death among cancer patients and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type. Cigarette smoking is the prevailing risk factor for NSCLC, nevertheless, this cancer is also diagnosed in never-smokers. B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) belongs to immunological checkpoints which are key regulatory molecules of the immune response. A growing body of evidence highlights the important role of BTLA in cancer. In our previous studies, we showed a significant association between BTLA gene variants and susceptibility to chronic lymphoblastic leukemia and renal cell carcinoma in the Polish population. The present study aimed to analyze the impact of BTLA polymorphic variants on the susceptibility to NSCLC and NSCLC patients' overall survival (OS).
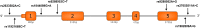
Methods: Using TaqMan probes we genotyped seven BTLA single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs): rs2705511, rs1982809, rs9288952, rs9288953, rs1844089, rs11921669 and rs2633582 with the use of ViiA 7 Real-Time PCR System.
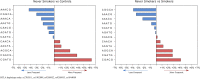
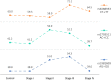
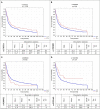
Results: We found that rs1982809 within BTLA is associated with NSCLC risk, where carriers of rs1982809G allele (AG+GG genotypes) were more frequent in patients compared to controls. In subgroup analyses, we also noticed that rs1982809G carriers are significantly overrepresented in never-smokers, but not in smokers compared to controls. Additionally, the global distribution of the haplotypes differed between the never-smokers and smokers, where haplotypes A G G C A, C G A C G, and C G A T G were more frequent in never-smoking patients. Furthermore, the presence rs1982809G (AG+GG genotypes) allele as well as the presence of rs9288953T allele (CT+TT genotypes) increased NSCLC risk in females' patients. After stratification by histological type, we noticed that rs1982809G and rs2705511C carriers were more frequent among adenocarcinoma patients. Moreover, rs1982809G and rs2705511C correlated with the more advanced stages of NSCLC (stage II and III), but not with stage IV. Furthermore, we showed that rs2705511 and rs1982809 significantly modified OS, while rs9288952 tend to be associated with patients' survival.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that BTLA polymorphic variants may be considered low penetrating risk factors for NSCLC especially in never-smokers, and in females, and are associated with OS of NSCLC patients.
Keywords: BTLA; NSCLC; SNP; disease risk; never-smokers; overall survival; smokers.
Copyright © 2023 Andrzejczak, Partyka, Wiśniewski, Porębska, Pawełczyk, Ptaszkowski, Kuśnierczyk, Jasek and Karabon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of 3' nearby gene BTLA polymorphisms with the risk of renal cell carcinoma in the Polish population.Urol Oncol. 2016 Sep;34(9):419.e13-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 May 24. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27234378
-
Intragenic Variations in BTLA Gene Influence mRNA Expression of BTLA Gene in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients and Confer Susceptibility to Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016 Dec;64(Suppl 1):137-145. doi: 10.1007/s00005-016-0430-x. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016. PMID: 27933341 Free PMC article.
-
Association of BTLA rs1982809 polymorphism with lung cancer risk in Tunisian population.Int J Immunogenet. 2020 Dec;47(6):554-562. doi: 10.1111/iji.12491. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Int J Immunogenet. 2020. PMID: 32757486
-
Non-small cell lung cancer in never smokers as a representative 'non-smoking-associated lung cancer': epidemiology and clinical features.Int J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug;16(4):287-93. doi: 10.1007/s10147-010-0160-8. Epub 2011 May 13. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21562939 Review.
-
Effect of smoking status on progression-free and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving erlotinib or gefitinib: a meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015 Dec;40(6):661-71. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12332. Epub 2015 Nov 17. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015. PMID: 26573867
Cited by
-
BTLA biology in cancer: from bench discoveries to clinical potentials.Biomark Res. 2024 Jan 17;12(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00556-2. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 38233898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical significance of endoplasmic reticulum stress related genes in non-small cell lung cancer and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism for CAV1.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Aug 6;11:1414164. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1414164. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39165641 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory gene polymorphisms in non-small cell lung carcinoma susceptibility and survival.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 13;10(12):e33003. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33003. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39021960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Methylation in B7-H4 and BTLA Genes are Associated with the Risk of Pulmonary Tuberculosis.Immunotargets Ther. 2023 Nov 24;12:149-163. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S434403. eCollection 2023. Immunotargets Ther. 2023. PMID: 38033484 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of HVEM/CD160 Variations on the Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma Risk and Overall Survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 22;25(13):6860. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136860. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38999968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gco.iarc.fr (2022). Cancer today. Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (Accessed 9 April 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

