Is there any relationship between red blood cell distribution width and prognosis of brain death?
- PMID: 36741490
- PMCID: PMC9878916
- DOI: 10.22088/cjim.14.1.37
Is there any relationship between red blood cell distribution width and prognosis of brain death?
Abstract
Background: Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that RDW (red blood cell distribution width) may independently predict clinically important outcomes in many populations. However, the role of RDW has not been elucidated in brain death. We conducted this study with the aim of evaluating the predictive value of RDW in brain death.
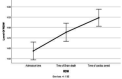
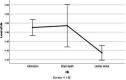
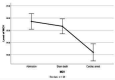
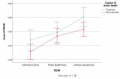
Methods: A retrospective study of seventy-seven of brain death cases during 36 months were evaluated at university hospitals, affiliated in Tehran, Iran. Demographical data include age, sex, BMI and cause of brain death, also laboratory results (red blood cell distribution, mean corpuscular volume, hemoglobin) collected by checklists from patient records. Having the three RDW measurements (days of hospital admission, day of brain death, and day of cardiac arrest) required.
Results: Time interval from hospital admission until brain death was 5.27±4.07. The mean age of brain death cases was 32.65±16.53. The mean RDW values on days of hospital admission, the day of brain death, and the day of cardiac arrest were 14.53±1.98, 15.12±1.93 and 15.18±2.07, respectively. Results of the repeated-measures ANOVA test reveal that RDW level was constantly higher in the traumatic patient group compared to the non-traumatic ones (P=0.008).
Conclusion: The frequency of brain death was high in patients with high RDW values. RDW might be a prognostic biomarker for brain death. More prospective studies with large sample size and long follow-up period should be carried out to determine the prognostic significance of RDW and brain death in future.
Keywords: Brain death; Cardiac arrest; RDW.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between red blood cell distribution width and the prognosis of brain death in patients with a Glasgow Coma Scale < 6.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 28;13(1):14027. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39836-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37640749 Free PMC article.
-
Red Cell Distribution Width in Diagnosis of Brain Death.Transplant Proc. 2019 Sep;51(7):2189-2191. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2019.04.072. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Transplant Proc. 2019. PMID: 31371213
-
Elevated red blood cell distribution width predicts mortality in acute exacerbation of COPD.Pneumologia. 2016 Apr-Jun;65(2):85-9. Pneumologia. 2016. PMID: 29542313
-
Utility of Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) as a Noninvasive Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 5222 Cases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 17;12(4):1011. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12041011. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of admission red blood cell distribution width in acute pancreatitis: a systematic review.Ann Transl Med. 2017 Sep;5(17):342. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.06.61. Ann Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28936436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gastala J, Fattal D, Kirby PA, et al. Brain death: Radiologic signs of a non-radiologic diagnosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019;185:105465. - PubMed
-
- Latifi M, Bagherpour F, Jafarian A, Hamidiyeh A, Javandoost E, Mansouri Z, et al. Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on organ donation and transplantation activities in Iran. Korean Journal of Transplantation. 2021;35(Supple 1):S172.
-
- Wong J, Tan HL, Goh JPS. Management of the brain dead organ donor. Trends Anaesth Crit Care. 2017;13:6–12.
-
- Smukowska-Gorynia A, Tomaszewska I, Malaczynska-Rajpold K, et al. Red blood cells distribution width as a potential prognostic biomarker in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Heart Lung Circ. 2018;27:842–8. - PubMed
-
- Latifi M, Bagherpour F, Rahban H, Pourhossein E, Dehghani S. Brain death hormone therapy and Graft survival: a systematic review of the literature. Transplantation Reports. . 2022:100098.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
