A Comparative Study of Sublingual Misoprostol Versus Intramuscular Oxytocin in the Active Management of Third Stage of Labor
- PMID: 36741612
- PMCID: PMC9896297
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33339
A Comparative Study of Sublingual Misoprostol Versus Intramuscular Oxytocin in the Active Management of Third Stage of Labor
Abstract
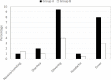
Objective Misoprostol has attracted low-income low-resource countries for the active management of the third stage of labor. The objective of this study was to compare the efficacy of sublingual misoprostol and intramuscular oxytocin in the active management of the third stage of labor. Study design This was a prospective randomized controlled trial in which a total of 407 healthy pregnant women having singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation, and normal vaginal delivery were divided into two groups. In the first group (n=203), women received 600 µg misoprostol tablet sublingually, and in the second group (n=204), women received 10 IU of intramuscular oxytocin, within 1 minute of the delivery of the baby during the third stage of labor. Three patients from the first group and four patients from the second group were excluded from the analysis due to traumatic postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). The primary outcome was an incidence of PPH. Secondary outcomes were the duration of the third stage of labor, amount of blood loss, fall in hemoglobin concentration after 48 hours of delivery, need for additional uterotonics, and side effects of the drugs. Data were compared using the chi-square and independent samples t-test. Results The incidence of PPH was 6.5% in the misoprostol group as compared to 2% in the oxytocin group (p=0.026). The misoprostol group also had significantly higher blood loss (293.75±125.8 mL) and a greater fall in hemoglobin level (0.58±0.25 g/dL) as compared to that in the oxytocin group (226.13±98.44 mL and 0.45±0.20 g/dL) (p<0.001). The mean duration of the third stage of labor was significantly higher in the misoprostol group (5.31±2.1 min) as compared to that in the oxytocin group (3.65±1.75 min) (p<0.001). The additional need for uterotonics was recorded in 15% of the study participants in the misoprostol group as compared to 8% in the oxytocin group (p=0.028). The incidence of side effects such as shivering and fever was significantly higher in the misoprostol group as compared to the oxytocin group. No significant difference between the two groups was observed concerning the incidence of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headache. Conclusion Intramuscular oxytocin is a safe and useful alternative to sublingual misoprostol in facilitating the third stage of labor with minimal blood loss, fewer incidences of hemorrhage, and fewer adverse effects.
Keywords: oxytocin; postpartum hemorrhage; sublingual misoprostol; third stage of labor; uterotonics.
Copyright © 2023, Mishra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sublingual misoprostol versus intramuscular oxytocin for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage in Uganda: a double-blind randomized non-inferiority trial.PLoS Med. 2014 Nov 4;11(11):e1001752. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001752. eCollection 2014 Nov. PLoS Med. 2014. PMID: 25369200 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Study to Compare the Efficacy of Misoprostol, Oxytocin, Methyl-ergometrine and Ergometrine-Oxytocin in Reducing Blood Loss in Active Management of 3rd Stage of Labor.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2011 Aug;61(4):408-12. doi: 10.1007/s13224-011-0060-5. Epub 2011 Sep 23. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2011. PMID: 22851822 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Misoprostol 600 mcg Oral in Active Management of Third Stage of Labor: A Comparative Study with Oxytocin 10 IU i.m.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2013 Oct;63(5):325-7. doi: 10.1007/s13224-012-0330-x. Epub 2013 May 3. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2013. PMID: 24431668 Free PMC article.
-
Active management of the third stage of labour: prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009 Oct;31(10):980-993. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)34329-8. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009. PMID: 19941729 Review.
-
Evidence-based labor management: third stage of labor (part 5).Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022 Sep;4(5):100661. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2022.100661. Epub 2022 May 7. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022. PMID: 35537683 Review.
Cited by
-
A randomized controlled study comparing oral misoprostol with intramuscular oxytocin in active management of third stage of labour.Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2024 May;67(3):279-285. doi: 10.5468/ogs.23128. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38409787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO recommendations for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage. [ Oct; 2022 ]. 2012. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/75411/9789241548502_eng... https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/75411/9789241548502_eng... - PubMed
-
- Registration, procurement, distribution, and use of misoprostol in Uganda: an interview-based observational study. Atukunda EC, Brhlikova P, Agaba AG, Pollock AM. Lancet. 2013;382:10. - PubMed
-
- New and underutilized technologies to reduce maternal mortality: call to action from a Bellagio workshop. Tsu VD, Shane B. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2004;85 Suppl 1:0–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources