Does Zoledronic Acid Provide a Good Clinical Outcome in Patients With Chronic Back Pain Associated With Vertebral Osteoporosis?
- PMID: 36741620
- PMCID: PMC9894817
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33328
Does Zoledronic Acid Provide a Good Clinical Outcome in Patients With Chronic Back Pain Associated With Vertebral Osteoporosis?
Abstract
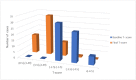
Background Osteoporosis is a chronic, progressive, systemic condition of the skeletal tissue that is characterized by reduced bone density, microarchitecture deterioration, and fragile bones, making osteoporotic fractures or fragility fractures more likely to occur. This condition often remains asymptomatic and undiagnosed until it presents with fragility fractures. The condition is associated with a significant socioeconomic burden with disability, morbidity, and mortality. Therefore, early diagnosis, as well as treatment, is needed to prevent fractures. Intravenous zoledronic is an effective bisphosphonate with high patient compliance due to once-yearly dosing. The present study aims to determine whether zoledronic acid effectively treats chronic back pain in people with osteoporosis. Materials and methods Seventy patients above the age of 60 years presented with complaints of chronic low back aches to the outpatient department of orthopedics, R L Jalappa Hospital & Research Centre attached to Sri Devaraj Urs Medical College. The study was conducted between November 2016 and November 2018. Results All the patients found excellent clinical improvement following zoledronic acid infusion in early and long-term follow-ups. Additionally, it was found that zoledronic acid's effectiveness was excellent, with significant improvement in bone mineral density (BMD), T-score, and Z-score. Conclusion Early diagnosis and treatment of vertebral osteoporosis is the most important factor in preventing fragility fractures. Zoledronic acid, an antiresorptive drug with better compliance, is very effective in controlling low back pain, improving bone mineral density, and preventing the occurrence of atraumatic fragility fractures. With all the above factors, zoledronic acid is a preferable bisphosphonate for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis compared to other modalities of treatment of osteoporosis.
Keywords: bisphosphonates; bone mineral density; bone remodeling; dual energy x-ray absorptiometry; fragility fractures; t-score; vertebral osteoporosis; zoledronic acid.
Copyright © 2023, M et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- The effect of parity on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: a systematic review. Bayray A, Enquselassie F. https://www.longdom.org/open-access-pdfs/the-effect-of-parity-on-bone-mi... J Osteopor Phys Act. 2013;1:104.
-
- Importance of recognition of osteoporosis and the radiologic diagnosis using DEXA technique. Aldosh M. J Osteopor Physical Act. 2017;5:206.
-
- Osteoporosis: a review of treatment options. Tu KN, Lie JD, Wan CK, et al. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5768298/ P T. 2018;43:92–104. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prevalence of osteopenia and osteoporosis in orthopaedic outpatients in Southern India. Chitten JJ, James B. J Clin Diagn Res. 2018;12:14–17.
-
- The prevalence of osteoporosis and osteopenia in persons above 50 years attending a tertiary care hospital in South India. Hemalata Hemalata, Reeba MM, Sreekala VK. J Med Sci Clin Res. 2016;4:14458–14462.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources